Introduction
The year 2025 constitutes a distinct structural watershed in the evolutionary trajectory of the cryptocurrency market. During this year, crypto assets transitioned from a stage dominated by fringe experimentation to becoming further embedded within the mainstream financial system. This shift was marked by structural adjustments across market participant composition, the ecosystem of trading instruments, and the regulatory environment.
The derivatives market achieved significant expansion in 2025, with its market structure becoming notably more complex. The early single-driver model, characterized by high-leverage retail speculation, has been replaced by more diversified institutional trading demands, ushering the market into a new phase defined by "the dominance of institutional capital and the parallel evolution of compliant infrastructure and decentralized technology." On one hand, traditional financial capital has entered the market on a larger scale and with clearer compliance pathways through channels such as BTC spot ETFs, options, compliant futures, and M&A integration. Demand for hedging and basis trading has gradually migrated toward exchange-traded products, driving a structural ascent for CME. After surpassing Binance in 2024 to become the global leader in BTC futures Open Interest, CME further consolidated its dominance in BTC derivatives in 2025. Furthermore, in the ETH derivatives market, CME approached the retail scale of Binance in terms of both Open Interest and trading volume for the first time. On the other hand, leveraging intent-centric architectures and high-performance application chains, on-chain derivatives have established a functional alternative to centralized derivatives in specific niche scenarios—particularly regarding censorship-resistant trading and the execution of composable strategies—beginning to exert substantive competitive pressure on Centralized Exchanges (CEXs) in marginal market shares.
Higher complexity and deeper leverage chains have simultaneously elevated systemic tail risks. Extreme events that erupted during 2025 imposed stress tests of unprecedented scale on existing margin mechanisms, liquidation rules, and cross-platform risk transmission pathways. The impact of these events extended beyond the scope of single assets or single platforms, necessitating a re-evaluation of the robustness of the entire derivatives ecosystem.
It is important to emphasize that the aforementioned shifts represent only a cross-section of the market restructuring in 2025. Beyond macro-narratives and extreme events, the rise of Perpetual DEXs (Perp DEXs), the massive expansion of stablecoins, the institutional exploration of Real World Assets (RWAs), the development of DAT architectures, the iteration of on-chain prediction markets, and the progressive implementation of regulatory frameworks across major jurisdictions collectively form the multidimensional background of this year. These internal structural evolutions, intertwined with external shock events, constitute the comprehensive landscape and the analytical starting point for the 2025 crypto derivatives market.
I.Market Overview
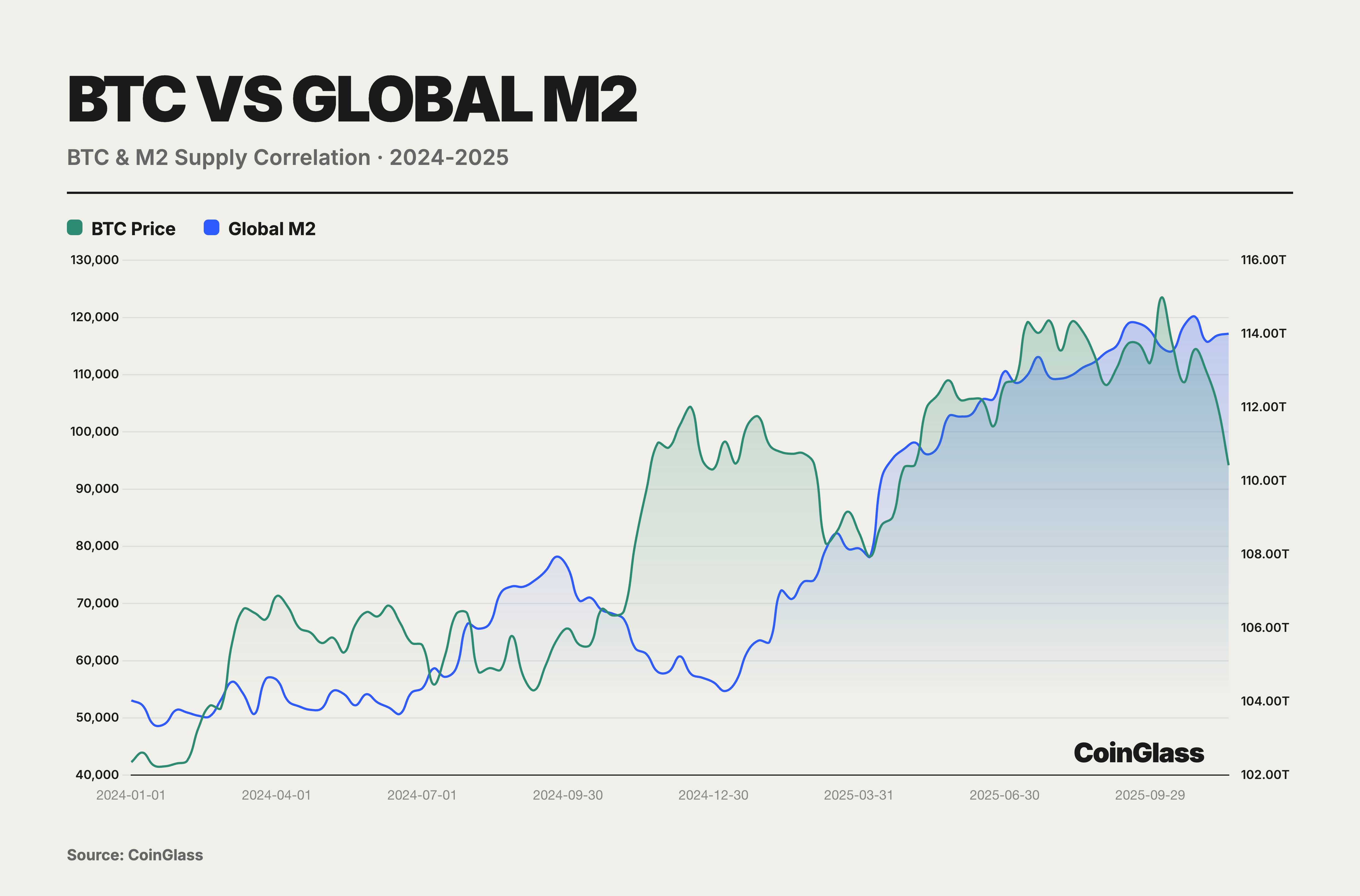
During the easing and bull market window of 2024–2025, BTC functioned more closely as a High-Beta risk asset rather than an independent inflation hedge. Although a full-year correlation of 0.78 with global M2 obscured a structural decoupling in the second half of the year, the decline in November validated its intrinsic nature as a High-Beta risk asset. Purchasing BTC was not an act of hedging against inflation but rather a long position on liquidity; consequently, BTC is liable to be the first asset liquidated upon any tightening of liquidity conditions. Against the backdrop of the Federal Reserve initiating a rate-cutting cycle and substantial liquidity injections by global central banks, BTC surged from $40,000 to $126,000. These excess returns stemmed essentially from a Beta coefficient of 2.5–3.0,representing a leveraged response to liquidity expansion,rather than independent value discovery.
Geopolitical and policy uncertainties emerged as critical market influencers in 2025, while the complexity of the macroeconomic environment throughout the year provided an extremely rich set of trading narratives for the derivatives market. Factors such as the reignited trade friction between the United States and China, the Federal Reserve’s arduous balancing act between rate cuts and recurring inflation, the unwinding of carry trades triggered by the Bank of Japan’s monetary policy normalization, and the aggressive crypto-friendly policies of the new U.S. administration coalesced into a complex macroeconomic force. This confluence injected sustained volatility and created deep opportunities for strategic gaming within the derivatives market. Overall, cryptocurrencies continued to behave primarily as a risk asset class; specifically, as a High-Beta asset class, they demonstrated extreme sensitivity to global liquidity conditions and pivots in central bank policies throughout the year.
In 2025, cryptocurrency derivatives regulation across major jurisdictions exhibited a pattern of "directional convergence with divergent pathways." Under the leadership of the new administration, the United States shifted toward a regulatory framework centered on legislation and licensing, incorporating digital assets into its national financial strategy. Through a series of bills, including the GENIUS Act, the U.S. mitigated the sources of uncertainty previously caused by "regulation by enforcement." Meanwhile, the European Union, operating within existing frameworks such as MiCA and MiFID, continued to pursue a prudent path focused on consumer protection and leverage restrictions, enforcing stricter entry thresholds for high-leverage retail derivatives. Significant disparities persisted within the Asian region: Mainland China maintained its high-pressure stance against cryptocurrency trading, whereas Hong Kong and Singapore positioned themselves as compliant testing grounds, competing for institutional pricing and settlement business through licensing regimes and product whitelists. Notably, the Singapore Exchange (SGX) launched BTC and ETH Perpetual futures, marking the integration of select crypto-native products into traditional financial infrastructure. The UAE, leveraging a unified digital asset regulatory framework, accelerated its attraction of crypto enterprises and trading platforms, establishing itself as a regional compliance hub. On a holistic level, regulation targeting DeFi derivatives is gradually coalescing around the principle of "same activity, same risk, same regulation," foreshadowing a progressive convergence of compliance requirements for both on-chain and off-chain markets.
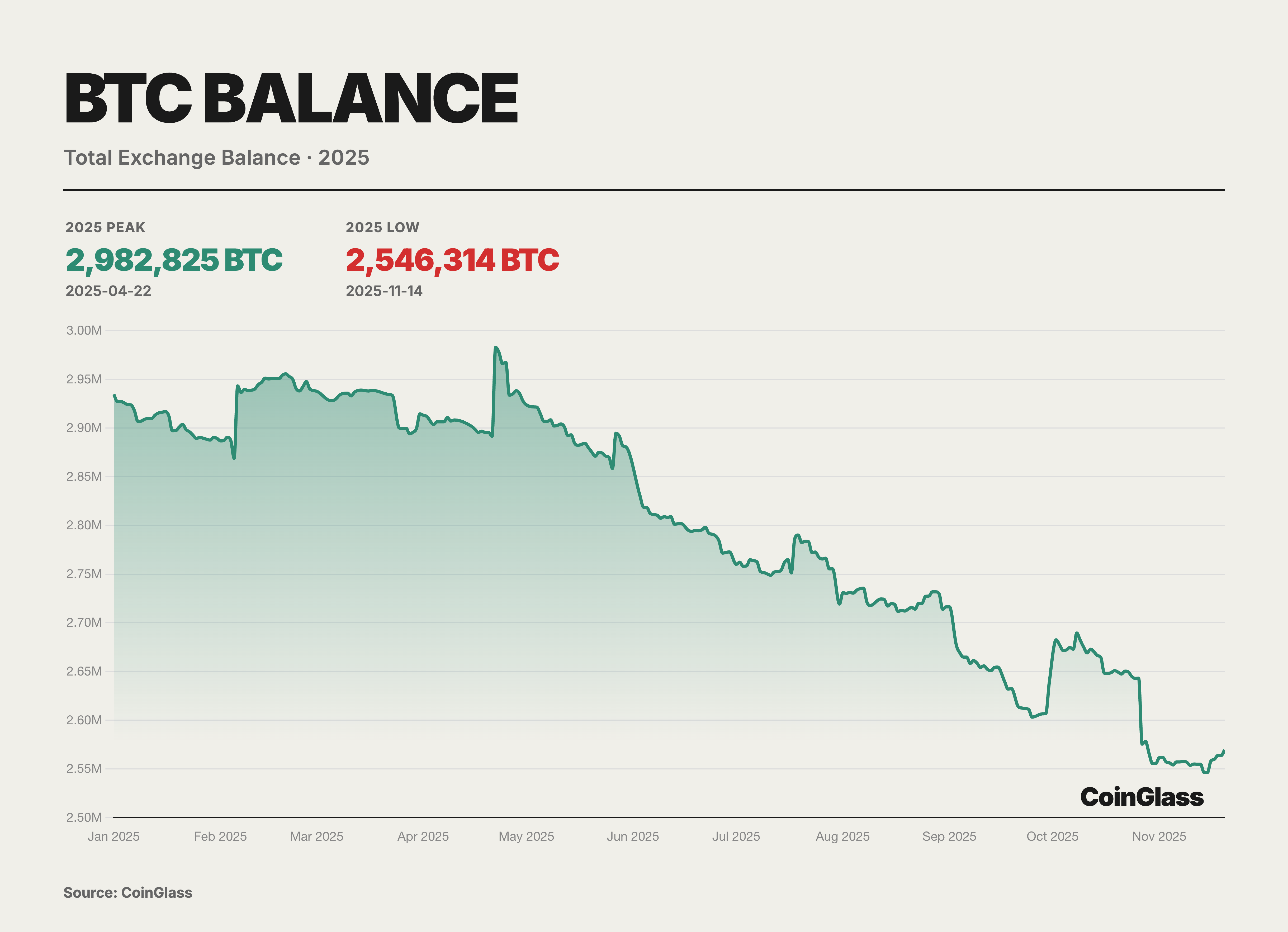
In 2025, BTC exhibited distinct signs of supply structure rebalancing at the exchange level, with overall exchange balances showing a step-wise downward trend and entering a phase of sustained destocking starting from the April highs. Data from CoinGlass indicates that after reaching an annual peak of approximately 2.98 million BTC around April 22, exchange BTC reserves followed a general step-wise decline over the subsequent months, dropping to approximately 2.54 million BTC by mid-November,a net outflow of roughly 430,000 BTC, representing a decrease of about 15%.
This cycle of destocking reflects a migration of holdings from exchanges to self-custody addresses and a structural shift in trading demand toward "low turnover, long-term holding," rather than merely a reduction in short-term selling pressure. While the continuous withdrawal of tradable supply from exchanges helps elevate marginal transaction prices and amplify pro-cyclical gains during upward phases, it crucially implies that should macroeconomic expectations or price trends reverse, a concentrated reflux of previously withdrawn reserves could generate amplified selling pressure and volatility against a thinner order book.
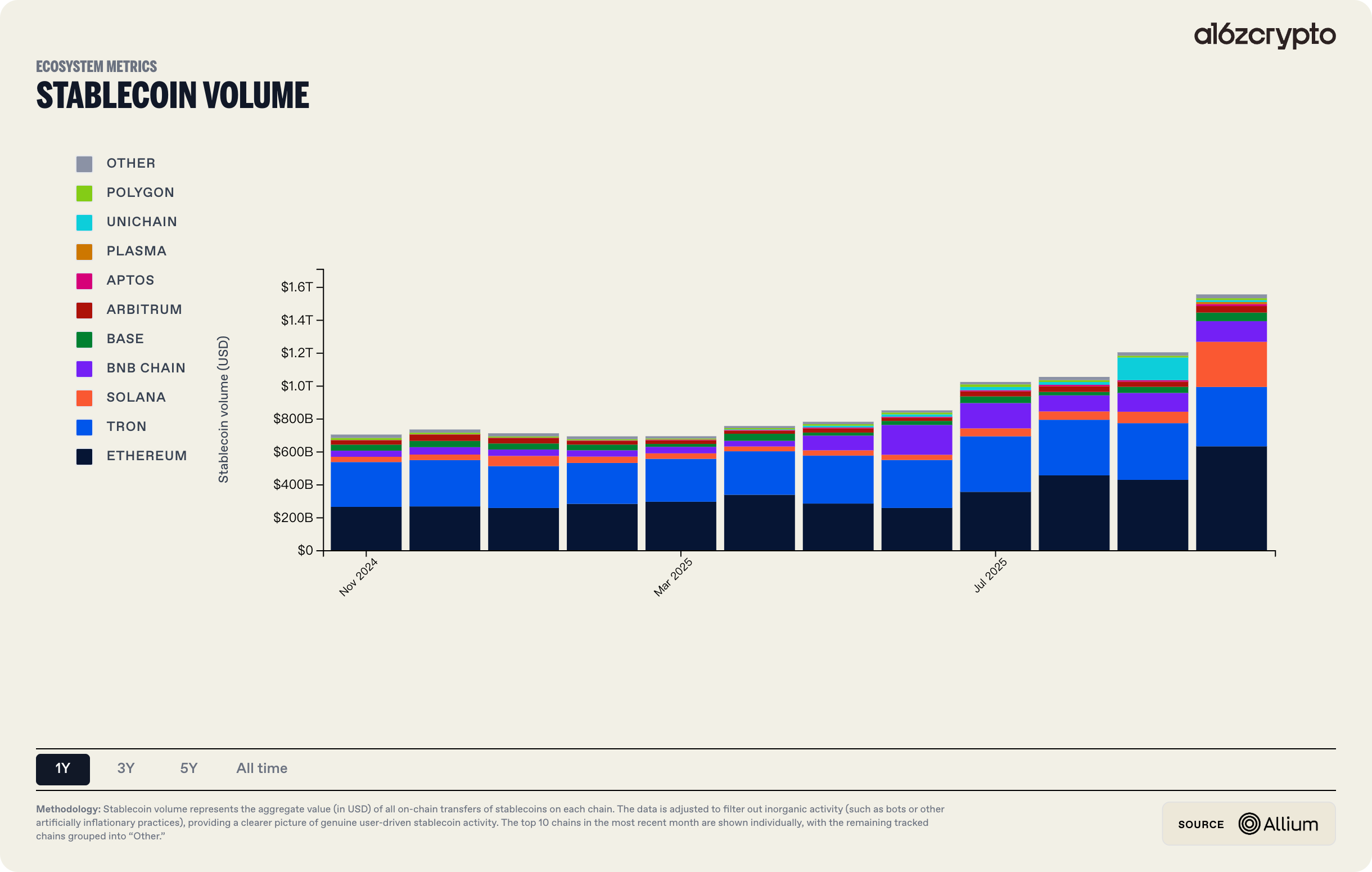
In 2025, the volume and application scenarios for stablecoins and DATs expanded synchronously, beginning to interface directly with traditional finance at the foundational level. The total market capitalization of stablecoins temporarily breached $230 billion, with an annual on-chain settlement volume of approximately $1.5 trillion. Underpinned by legislation such as the GENIUS Act, stablecoins have progressively solidified their role as the underlying settlement layer for cross-border payments and on-chain finance. Simultaneously, the DAT model, utilizing compliant equity or fund vehicles, provided traditional institutional investors with a standardized pathway to access crypto asset exposure; at their peak, DAT-held BTC and ETH assets exceeded $140 billion in market value, representing a year-on-year increase of over three times. Real World Assets (RWAs) acted as a critical intermediary in this ecosystem, anchoring real-world asset cash flows on one end while connecting to the on-chain settlement and valuation systems of stablecoins and DATs on the other. The BCG–Ripple 2025 Report projects that the tokenized asset market will expand from its current level of approximately $600 billion to nearly $18.9 trillion by 2033, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of roughly 53%, thereby providing a foundational scale hypothesis for this evolution.
The year 2025 also marked a pivotal inflection point where decentralized derivatives transitioned from proof-of-concept to competing for actual market share. Mainstream on-chain derivative protocols made substantive progress in technical architecture, product morphology, and interaction experience, beginning to form a viable alternative to the trading and listing advantages of Centralized Exchanges (CEXs). High-performance application chain architectures, represented by Hyperliquid, validated that decentralized infrastructure can compete directly with centralized matching platforms in specific scenarios regarding throughput, latency, and capital efficiency. Furthermore, "Intent-centric" architecture emerged as the core paradigm for DeFi experience upgrades in 2025: users need only specify a target state, after which Solvers or AI agents conduct a competitive search for the optimal execution path off-chain before submitting a unified settlement on-chain, significantly lowering the operational barriers for complex transactions.
In 2025, the migration of RWAs on-chain became a significant marker of the crypto industry's stride toward the mainstream. Growth momentum stemmed primarily from two sources: first, the marginal easing of the regulatory environment, as the United States strove to reshape its status as a crypto financial hub, with U.S. Treasuries and stocks becoming the core assets for initial tokenization; and second, strong organic demand—a vast number of global investors lack direct, convenient channels to trade U.S. stocks, and tokenization partially lowered the entry barriers imposed by nationality and geography. Data from Token Terminal indicates that the market capitalization of stock tokens grew by 2,695% in 2025.
Concurrently, the brand effects of top-tier issuance and trading platforms gradually became apparent. Representative players in the RWA narrative emerged, such as Ondo and xStocks, which utilized on-chain accessible traditional financial assets as their entry point. Meanwhile, mainstream exchanges like Bitget and Bybit continued to invest resources in the listing, trading, and liquidity support of related assets. Superimposed with experiential advantages such as the elimination of tedious account opening processes and 24/7 tradability, stock tokens became a direction of significantly heightened market attention in 2025. A Bitget report revealed that during Q3 2025, its stock contract trading volume grew 4,468% quarter-over-quarter, with cumulative trading volume surpassing $10 billion.
Against a backdrop where macro-narratives and regulatory frameworks were progressively clarified and uncertainty converged, more complex trading structures and gaming spaces were unlocked. Based on this macroeconomic and institutional context, Part II will turn to an empirical profile of centralized trading infrastructure. Through quantitative tracking of spot and derivatives trading volume distribution across mainstream CEXs, changes in market share, and capital flows into BTC Spot ETFs, this section will delineate the capital allocation paths of various participants, the structural reshuffling of market share among trading platforms, and the reshaping of overall market liquidity and price discovery mechanisms by the entry of institutional capital in 2025.
II.Centralized Derivatives Exchanges
- CEX Derivatives Trading Volume
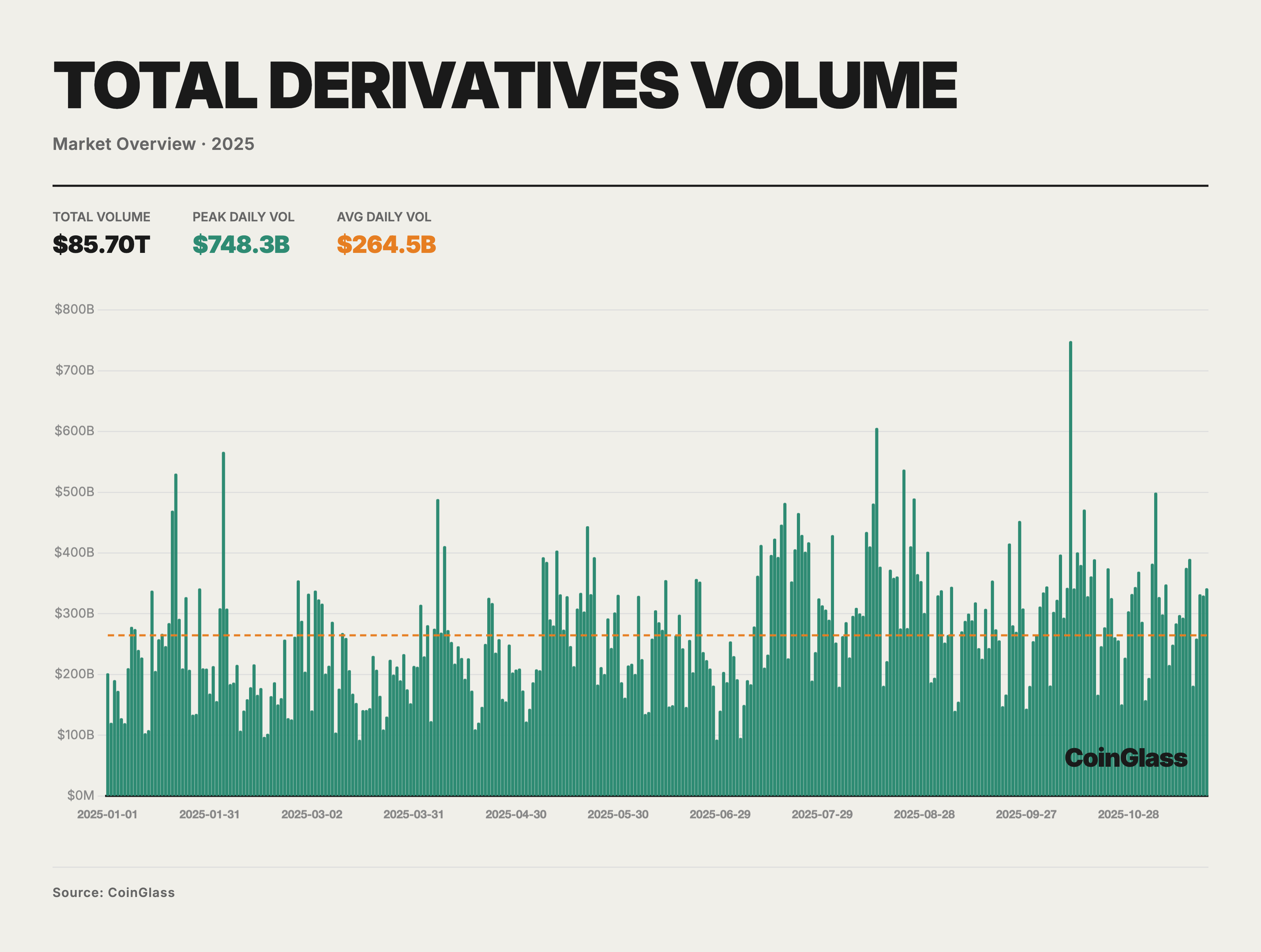
In 2025, the total trading volume of the cryptocurrency derivatives market reached approximately $85.70 trillion, with a daily average turnover of about $264.5 billion. Against a backdrop of a persistently tight macro-liquidity environment interspersed with episodic recoveries in risk appetite, annual trading activity generally exhibited a structure characterized by a "low start, high finish, and oscillating upward trend." Currently, derivatives have established themselves as the primary venue for price formation and risk management for the vast majority of mainstream assets. High-volume trading days appeared repeatedly above the average line (indicated by the orange dashed line in the chart); notably, the single-day peak on October 10 reached approximately $748 billion—significantly higher than the annual norm. This reflects that during phases of market acceleration, derivatives have become the core battlefield for price discovery and leveraged speculation. From a monthly perspective, daily average trading volume mostly hovered around $200 billion in the first quarter, gradually rose starting in the second quarter, and elevated to a level above $300 billion in July–August and October.
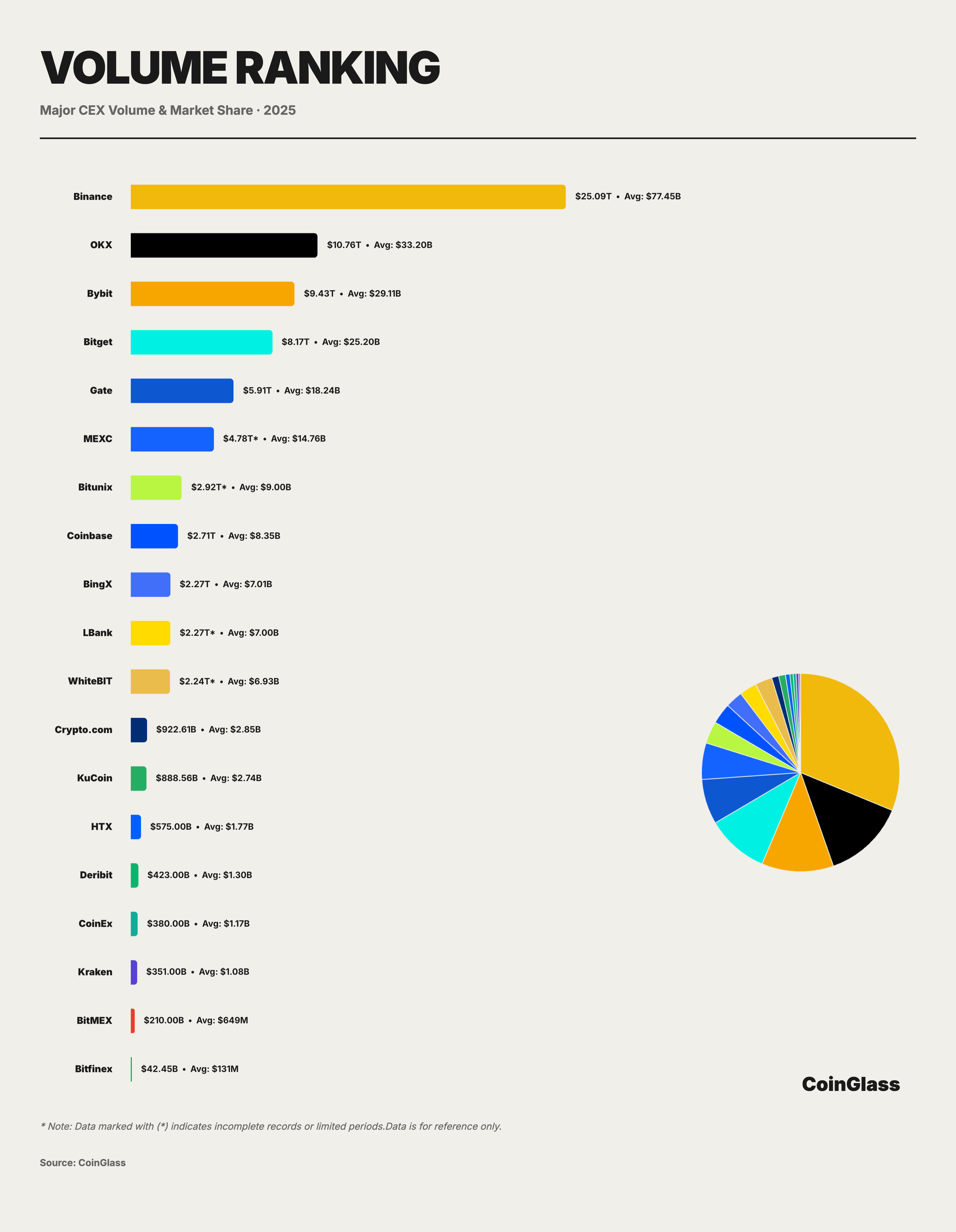
Behind the total trading volume of $85.70 trillion and the daily average of $264.5 billion, the distribution of market share exhibits characteristics of high concentration. Binance firmly occupies the market leadership position with a cumulative trading volume of $25.09 trillion and a daily average of $77.45 billion. Its market share stands at approximately 29.3%, implying that for every $100 traded in the global derivatives market, roughly $30 is executed on Binance.
The competitive landscape of the second tier presents distinct differentiation. OKX, Bybit, and Bitget follow closely behind, with cumulative trading volumes ranging between $8.2 trillion and $10.8 trillion, and daily averages varying from $25 billion to $33 billion. Together with Binance, their combined market share accounts for approximately 62.3% of the total market. OKX ranks second with a total volume of $10.76 trillion and a daily average of $33.20 billion, capturing a market share of roughly 12.5%. Bybit follows with a cumulative trading volume of $9.43 trillion and a daily average of $29.11 billion, holding a market share of approximately 11%. Bitget occupies the fourth position with a total volume of $8.17 trillion and a daily average of $25.20 billion, representing a market share of about 9.5%.
Gate ranks fifth with $5.91 trillion in total volume and a daily average of $18.24 billion, with its market share decreasing to approximately 6.9%. Although Gate, as a legacy exchange, maintains a certain volume, the gap between it and the top three is widening. More worthy of attention is the structural gap (or stratification) appearing after Gate: BingX's volume of $2.27 trillion is less than 40% of Gate's, while Crypto.com and KuCoin have fallen to the hundred-billion-dollar level ($922.61 billion and $888.56 billion, respectively), amounting to merely 3–4% of Binance's volume. Long-tail platforms such as Crypto.com and KuCoin each hold a market share of around 1%; they largely fulfill service functions for regional or niche client segments, and their pricing power and liquidity stickiness are significantly weaker than those of the top-tier exchanges. Conversely, comparing year-over-year and month-over-month growth rates, Bitunix leads in both metrics with the steepest growth slope, positioning it as one of the fastest-growing platforms in terms of trading volume.
This cliff-like distribution reveals the "Matthew Effect" within the platform economy, where top-tier platforms leverage their liquidity advantages to form a self-reinforcing cycle. Small and medium-sized platforms face the imperative to establish differentiated positioning within niche markets; otherwise, they will confront sustained pressure from market share erosion.
2.CEX Derivatives Open Interest
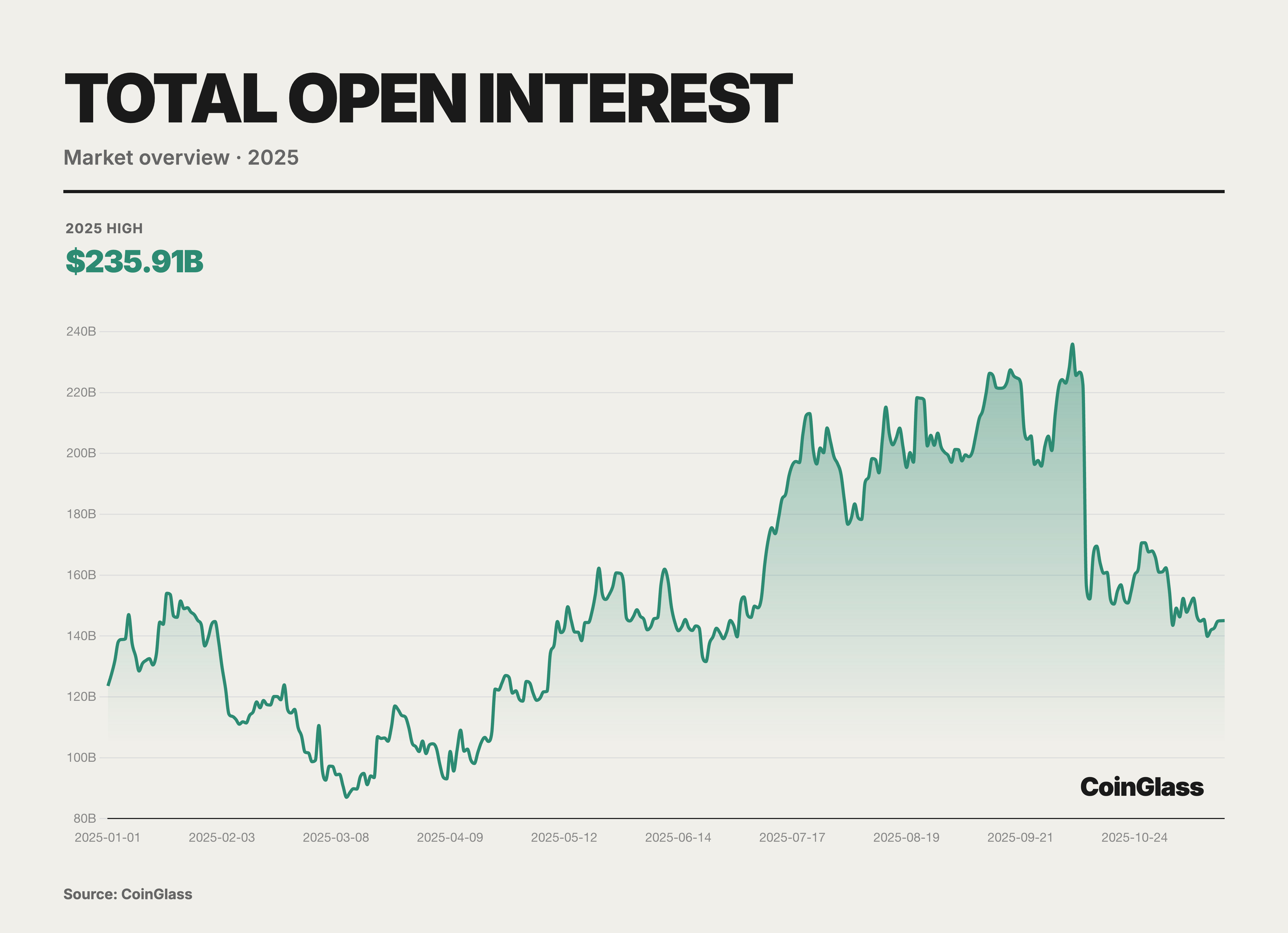
In 2025, global crypto derivatives Open Interest (OI) charted a volatile trajectory characterized by an initial suppression, a subsequent surge, and a final precipitous drop. Following a period of deep deleveraging in Q1, the market bottomed out at a yearly low of $87 billion due to prevailing panic. However, it immediately demonstrated exceptional resilience in Q2, completing a confidence rebuilding process that transitioned from hesitant testing to moderate position accumulation. By Q3, this recovery trend evolved into a near-frenzied accumulation of a leverage bubble; accelerated capital inflows drove OI on a unilateral upward trend until it touched a historical extreme of $235.9 billion on October 7. This highly crowded trading structure significantly elevated both the probability and intensity of a market correction. A flash deleveraging event in early Q4 wiped out over $70 billion in positions—accounting for one-third of the total OI—within a single day. Despite this, the year-end OI level of $145.1 billion still represented a 17% increase compared to the beginning of the year, with overall capital retention in the second half significantly exceeding that of the first half.
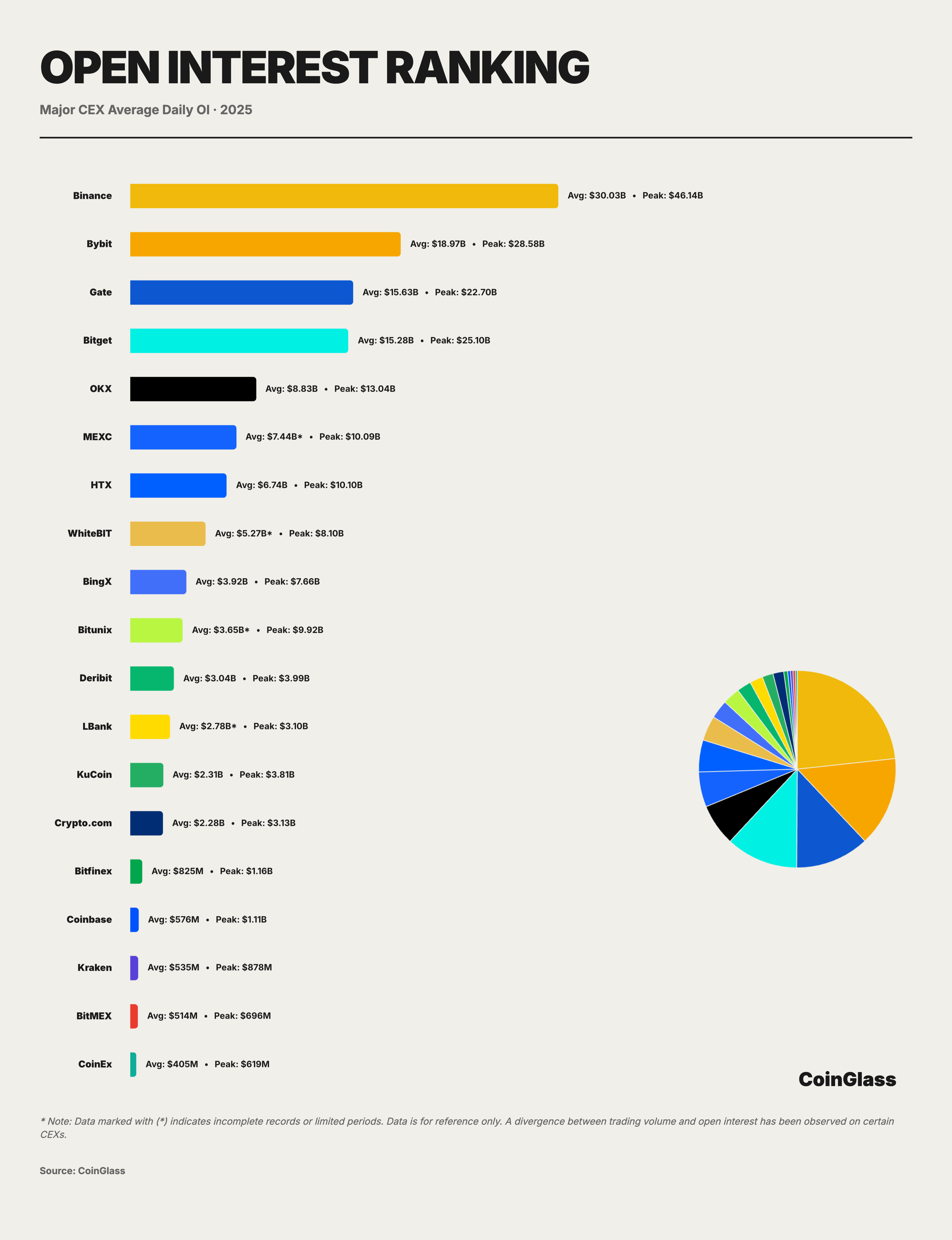
Based on daily average Open Interest data from major CEXs in 2025, the global derivatives market has solidified into a stratified oligopolistic landscape. The top ten centralized exchanges accounted for an aggregate daily average OI of approximately $108.3 billion. Binance secured a commanding lead with a daily average OI of approximately $30 billion, capturing a market share of about 28%. Bybit, Gate, and Bitget followed with approximately $19 billion, $15.6 billion, and $15.3 billion respectively. Collectively, these top four platforms controlled approximately 73% of the network-wide tradable leverage positions; when including OKX, the top five platforms accounted for over 80% of the OI, indicating an extremely high degree of concentration. Binance established a structural lead with a daily average roughly equivalent to the sum of the second and third runners-up, effectively serving as the decisive cornerstone of market liquidity. Closely following is the second tier composed of Bybit, Gate, and Bitget, all of which maintained high daily averages in the $15 billion to $19 billion range, together controlling half of the market. Notably, the gap between Gate and Bitget was only about $300 million, highlighting the extremely tight competition for market share between the two.
OKX's relatively lower Open Interest figures are attributable, in part, to the product architecture it offers, which provides high capital utilization rates. Capital on the platform rotates rapidly between different trading pairs and products, and is distributed across non-trading modules such as spot, wealth management, and staking; consequently, order book Open Interest metrics do not fully reflect the true scale of deposited capital. Furthermore, as a certain degree of divergence may exist between trading volume and Open Interest on some platforms, investors are advised to focus more on trading structure and capital distribution rather than relying solely on Open Interest indicators.
3.CEX Liquidity Depth
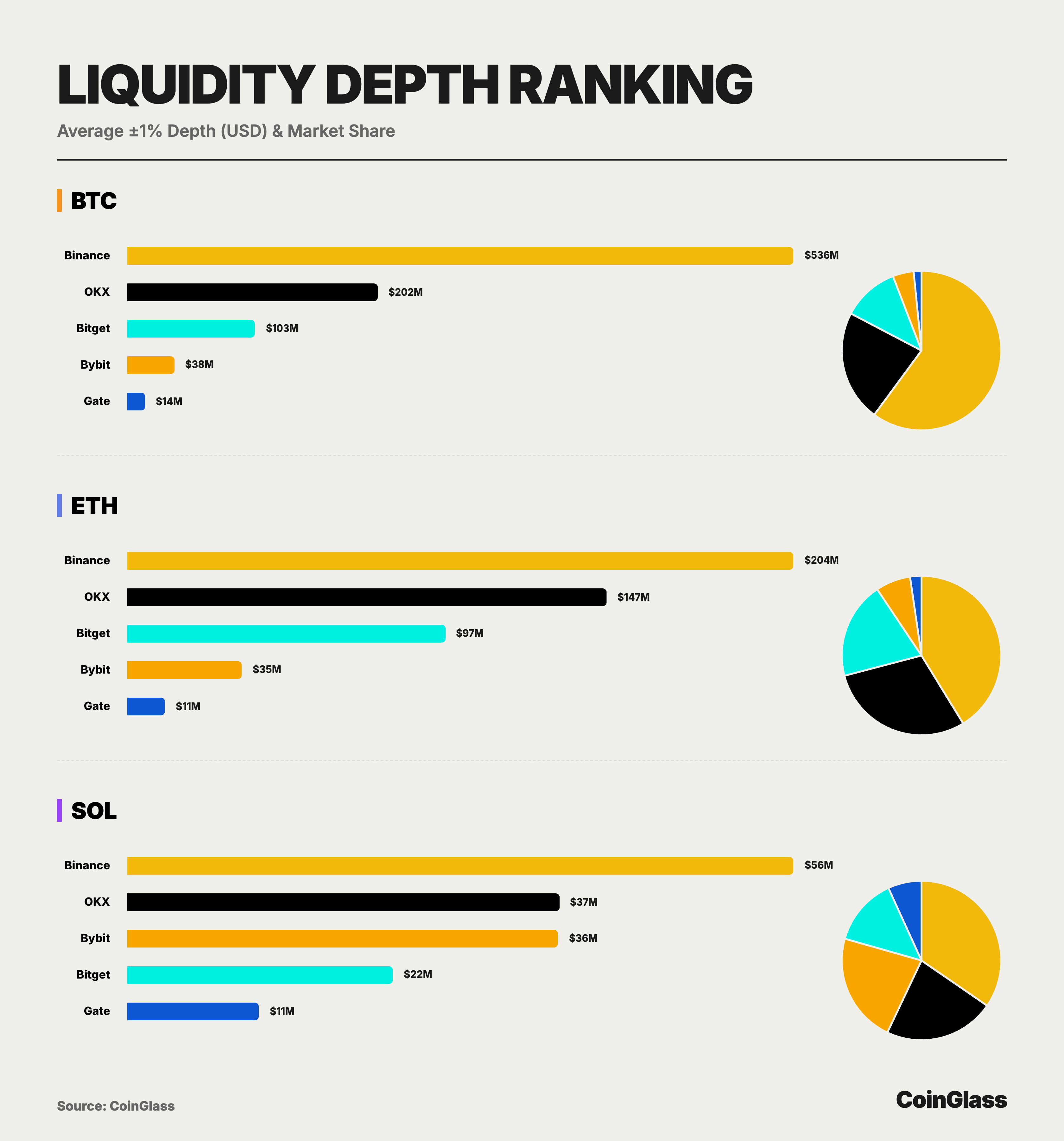
Based on the 2025 bilateral liquidity depth data for major assets (BTC/ETH/SOL), the market presents a structure distinct from that of Open Interest (OI). Binance undisputedly dominates the field with a staggering lead; its BTC liquidity depth of $536 million is not only 2.6 times that of the runner-up but also nearly equivalent to the combined total of the remaining four platforms, establishing its absolute status as the global liquidity hub for cryptocurrency derivatives. OKX, with a BTC depth of $202 million and an ETH depth of $147 million, demonstrates robust capability in accommodating large-scale transactions, proving that it remains the preferred venue for institutional and whale trading, second only to Binance.
Regarding BTC, Bitget ranks third with a bilateral depth of approximately $103 million—roughly 2.7 times that of Bybit and 7 times that of Gate—contributing nearly 11.5% to the total market BTC depth. In the ETH market, Bitget's ±1% depth stands at approximately $97.48 million, approaching 70% of OKX's level and significantly exceeding that of Bybit and Gate. Its contribution to the total market ETH depth is nearly 20%, thereby solidifying a liquidity distribution characterized by Binance's absolute leadership, OKX's firm second place, and Bitget's stable occupation of the core position in the second tier. Even for SOL, which possesses relatively weaker overall liquidity, Bitget provides a ±1% depth exceeding $22.42 million. This figure represents approximately 60% of the levels seen on OKX and Bybit and accounts for about 14% of the total market SOL depth, indicating that Bitget possesses considerable order absorption capacity even for high-volatility, relatively long-tail mainstream assets.
4.CEX User Asset Holdings
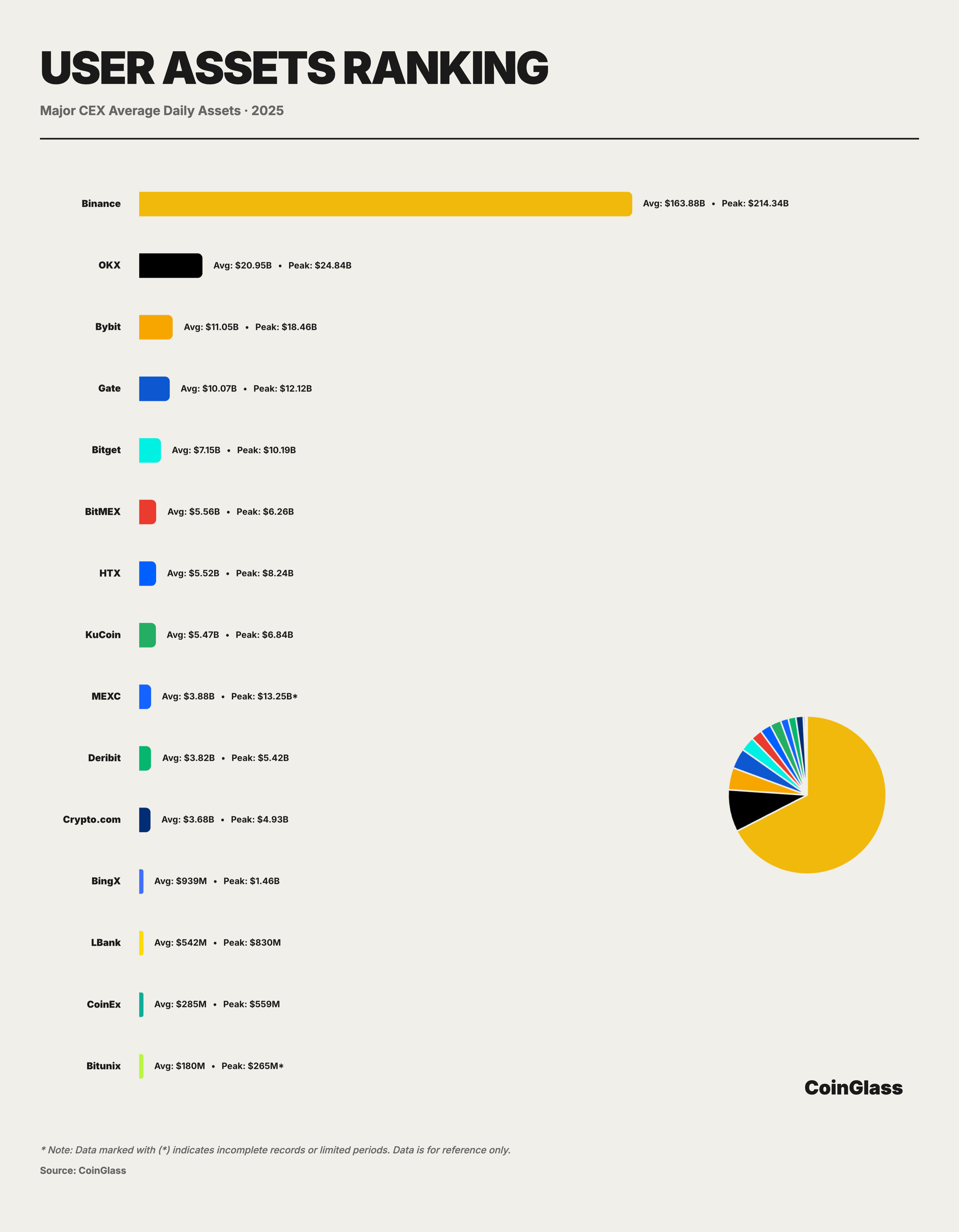
Based on 2025 user asset holding data, the crypto market exhibits a highly concentrated unipolar structure in terms of fund custody. Calculated using the Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI), the concentration of CEX custodial assets in 2025 stood at 5352, indicating that the cryptocurrency exchange market is in a state of extreme oligopoly. Binance dominates as the sole hegemon, capturing over 72% of the market share. With a daily average of approximately $163.9 billion in assets under custody and a yearly peak of about $214.3 billion, Binance exceeds the combined total of the next seven major platforms by 2.5 times. This level of concentration implies that, regarding actual fund storage and custody, Binance effectively assumes the role of "systemic infrastructure"; consequently, its operational and compliance status exerts an amplified effect on the robustness of the entire crypto market.
OKX ranks second with approximately $21 billion in daily average assets and a peak of $24.8 billion. Its scale is roughly double that of the third-place platform, Bybit, demonstrating OKX's advantage in user fund retention and medium-to-long-term asset accumulation. However, this structure—characterized by two poles followed by multiple mid-tier platforms—signifies that fund custody risks are highly concentrated within the top two platforms. Should either platform encounter a tail event at the compliance, technical, or operational level, the spillover effects would far exceed what their respective market shares might suggest.
Following this second tier, the market enters the fiercely competitive ten-billion-dollar range. Bybit, Gate, and Bitget recorded daily average assets of approximately $11.05 billion, $10.07 billion, and $7.15 billion, respectively, collectively constituting the sub-leading tier of asset holdings. Together, the top five platforms absorb over 90% of user assets, highlighting an extreme concentration of user funds.
5.CEX Rankings
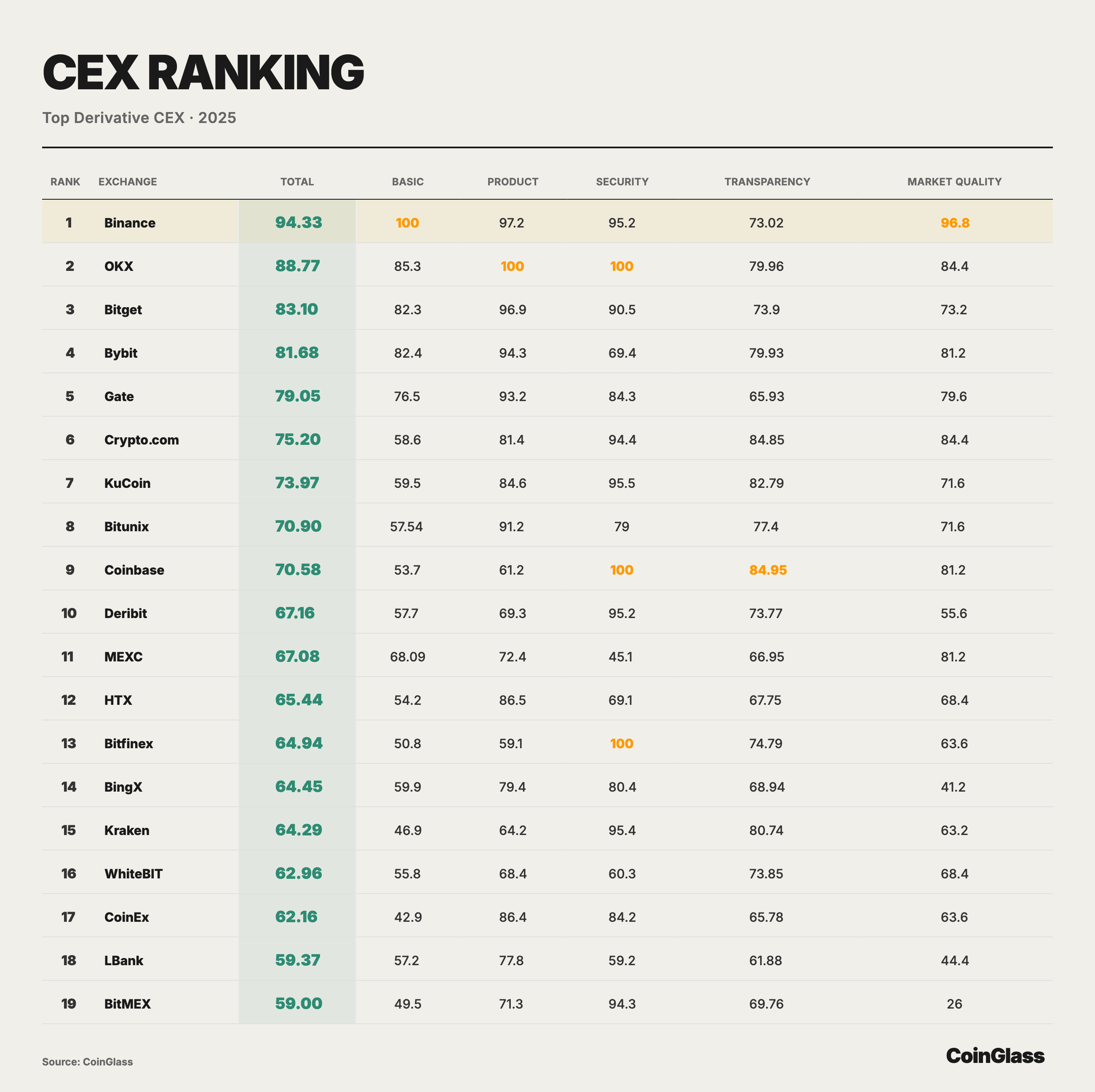
To shift the focus of derivatives trading concentration among top-tier CEXs from a purely volumetric narrative to a comparable qualitative dimension, CoinGlass conducted a comprehensive scoring and ranking of major derivatives CEXs. The chart below assigns core weighting to fundamental trading data and provides component scores and a weighted total score across dimensions such as product, security, transparency, and market quality. This intuitively presents the structural disparities among different platforms in terms of liquidity capacity, risk control constraints, and information disclosure.
 6.Liquidation Data
6.Liquidation Data
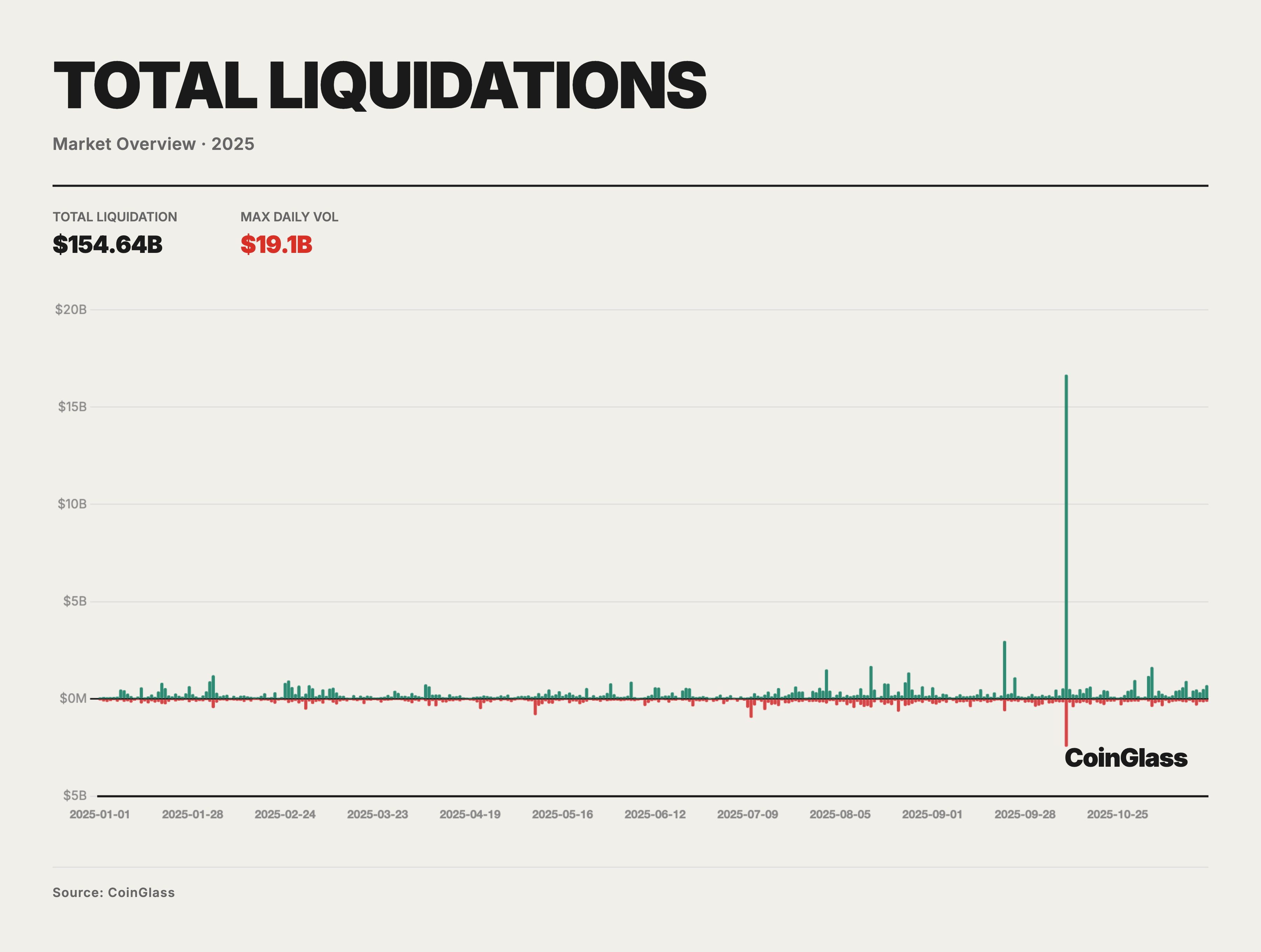
Throughout 2025, the total nominal value of forced liquidations across both long and short positions approximated $150 billion, corresponding to a daily average of roughly $400–500 million in routine leverage washing. On the vast majority of trading days, the scale of long/short liquidations remained within the range of tens to hundreds of millions of dollars, primarily reflecting daily margin adjustments and the clearing of short-term positions in a high-leverage environment; these movements had limited impact on medium-to-long-term prices and market structure. The systemic stress was truly concentrated within a few extreme event windows, with the deleveraging event of October 10–11 being the most archetypal.
On October 10, 2025, the market-wide liquidation volume reached an extreme peak within the sample period. Combined long and short liquidations exceeded $19 billion, far surpassing the single-day highs of all previous liquidation rounds. When factoring in the disclosure timing of certain platforms and feedback from market makers, the actual nominal liquidation scale likely approached $30–40 billion, representing a multiple of the second-highest event in the previous cycle. Structurally, the liquidations on that day were heavily skewed toward the long side, with long liquidations accounting for approximately 85–90% of the total. This indicates that prior to the event, BTC and related derivatives markets were in a state of extremely crowded long leverage.
From a causal perspective, the trigger for the October 10–11 event was an exogenous macroeconomic shock. On October 10, U.S. President Trump announced the imposition of 100% tariffs on imports from China effective November 1, alongside planned export controls on critical software. This significantly elevated market expectations for a new round of high-intensity trade warfare, causing global risk assets to immediately shift into a distinct "risk-off" mode. Prior to this, driven by easing expectations and expanding risk appetite, BTC had reached a historical high of approximately $126,000 in 2025. Long leverage utilization in the derivatives market was elevated, and the basis between spot and futures was high; consequently, the entire system was effectively in a fragile state characterized by "high valuation plus high leverage." Against this backdrop, the realization of negative exogenous macro news served as the direct catalyst that ignited the chain of concentrated liquidations.
The factor that truly determined the magnitude of the impact was the pre-existing leverage and product structure, as well as the design of liquidation mechanisms. Compared to three or four years prior, the market in 2025 featured a greater number of perpetual instruments with high Open Interest, more small-to-mid-cap assets, and more large-scale platforms, leading to a significant elevation in overall nominal leverage. Simultaneously, a large number of institutions adopted complex strategies involving long/short hedging, cross-asset, and cross-maturity positions. While these appeared as "risk-hedged" in terms of superficial exposure, they were in substance highly dependent on the orderly operation of liquidation engines and Auto-Deleveraging (ADL) mechanisms under extreme scenarios. Tail risks were not effectively managed. Once liquidation and risk management mechanisms deviated from their ideal trajectories under stress, the hedging legs that were supposed to offset each other were mechanistically dismantled, forcing portfolios originally constructed as neutral or low-net-exposure to be exposed as high-net directional positions.
After prices breached critical margin thresholds on October 10, standard trade-by-trade liquidation logic was initiated first. A massive volume of under-margined long positions was thrown into the order book for market-price liquidation, triggering the first round of concentrated deleveraging. As order book liquidity was rapidly consumed, the insurance funds of certain platforms struggled to fully absorb the losses, forcing the intervention of Auto-Deleveraging (ADL) mechanisms—a tool that had remained largely dormant over the long term. By design, ADL serves as a last line of defense in extreme situations where insurance funds are insufficient, forcibly reducing profitable opposing positions (shorts) to prevent prices from being driven to extreme levels by liquidation pressure, thereby avoiding platform insolvency. However, during this event, the execution of ADL exhibited significant deviations in price transparency and execution paths. Certain positions were forcibly reduced at prices significantly divergent from market rates. This caused the short positions of top-tier market makers, including Wintermute, to be passively closed at points far removed from fair value, rendering them virtually unable to hedge losses through normal trading. Concurrently, ADL triggers were concentrated primarily on altcoins with weaker liquidity and long-tail contracts, rather than on mainstream assets like BTC or ETH. This caused institutions employing structural strategies such as "Short BTC / Long Altcoins" to lose their short hedging legs within a short timeframe, rapidly exposing them to substantial downside risk in altcoin positions.
The deviant execution of liquidation and ADL mechanisms, superimposed with infrastructure-level issues, amplified the stress. Under extreme market conditions, multiple centralized platforms and on-chain channels experienced congestion in withdrawals and asset transfers. Cross-platform capital corridors were partially severed at critical moments, preventing the smooth execution of typical cross-exchange hedging paths. Consequently, even market makers willing to take the other side of the trade found it difficult to timely hedge risks on other platforms or markets. Under these circumstances, professional liquidity providers were forced to widen spreads or temporarily withdraw from the market for risk control purposes, further ceding price discovery to the automated logic of liquidation engines and ADL. Meanwhile, under high-load conditions, matching engines and API interfaces on certain CEXs experienced lag or even brief outages. Given that the crypto market lacks the clear circuit breakers and call auction mechanisms found in traditional stock and futures markets, prices were forced to slide further on order books dominated by passive liquidations, thereby exacerbating tail volatility.
In terms of outcomes, the impact of this event on different assets and platforms was highly uneven, yet we believe its long-term implications are significantly underestimated. Mainstream assets like BTC and ETH saw maximum drawdowns roughly in the 10–15% range, whereas a vast number of altcoins and long-tail assets experienced extreme retracements of 80% or even approached zero. This reflects that the liquidation chain and ADL execution produced the most severe price distortions on assets with the poorest liquidity. In contrast to the Terra/3AC era of 2022, this event did not trigger large-scale chain defaults among institutions. While market making firms like Wintermute sustained partial losses due to the ADL mechanism, their overall capitalization remained adequate. Risks were more concentrated within specific strategies and assets rather than diffusing throughout the entire system via a complex market structure.
III.Exchange-Traded Derivatives and DAT
- Exchange-Traded Derivatives
Fiscal Year 2025 was not merely a watershed moment in the history of digital asset development; it was the pivotal year in which CME firmly established its status as the global center for cryptocurrency pricing and risk transfer. If 2024 marked the inaugural year of access for spot ETFs, then 2025 represented the year of deepening for the exchange-traded derivatives market. Throughout this year, we witnessed a shift in institutional capital from purely passive allocation to active management utilizing complex derivatives strategies. Consequently, the liquidity moat between the compliant exchange-traded market and the unregulated offshore market was fundamentally reconstructed.
The most disruptive product innovation of 2025 was undoubtedly the launch and widespread adoption of Spot-Quoted Futures (tickers: QBTC and QETH). Distinct from traditional futures, these contracts are designed to provide a tighter peg to spot prices through specialized settlement mechanisms, thereby significantly reducing basis risk and roll costs.
With the launch of real-time data for the CME BTC Volatility Index (BVX), it is highly probable that the market will welcome tradable volatility futures in 2026. This development will grant institutional investors, for the first time, a tool to directly hedge against unknown risks without the need to simulate such exposure through complex option portfolios.
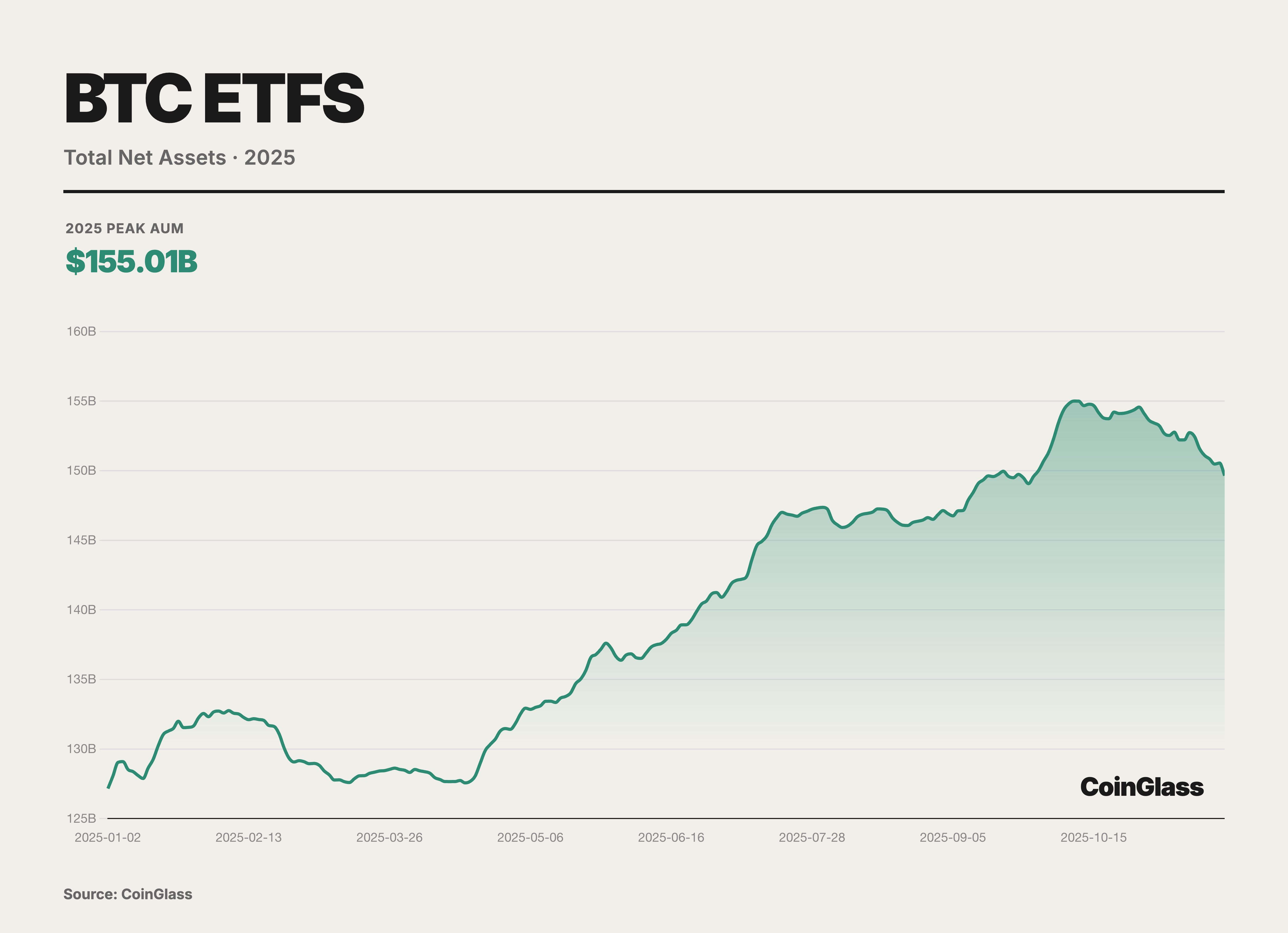
In 2025, we witnessed the normalization and massive scaling of basis trading. With the exponential growth in the Assets Under Management (AUM) of spot ETFs, the execution of cash-and-carry arbitrage using CME futures has not only become a mainstream strategy for hedge funds but also serves as a critical nexus connecting traditional financial interest rates with crypto-native yields.
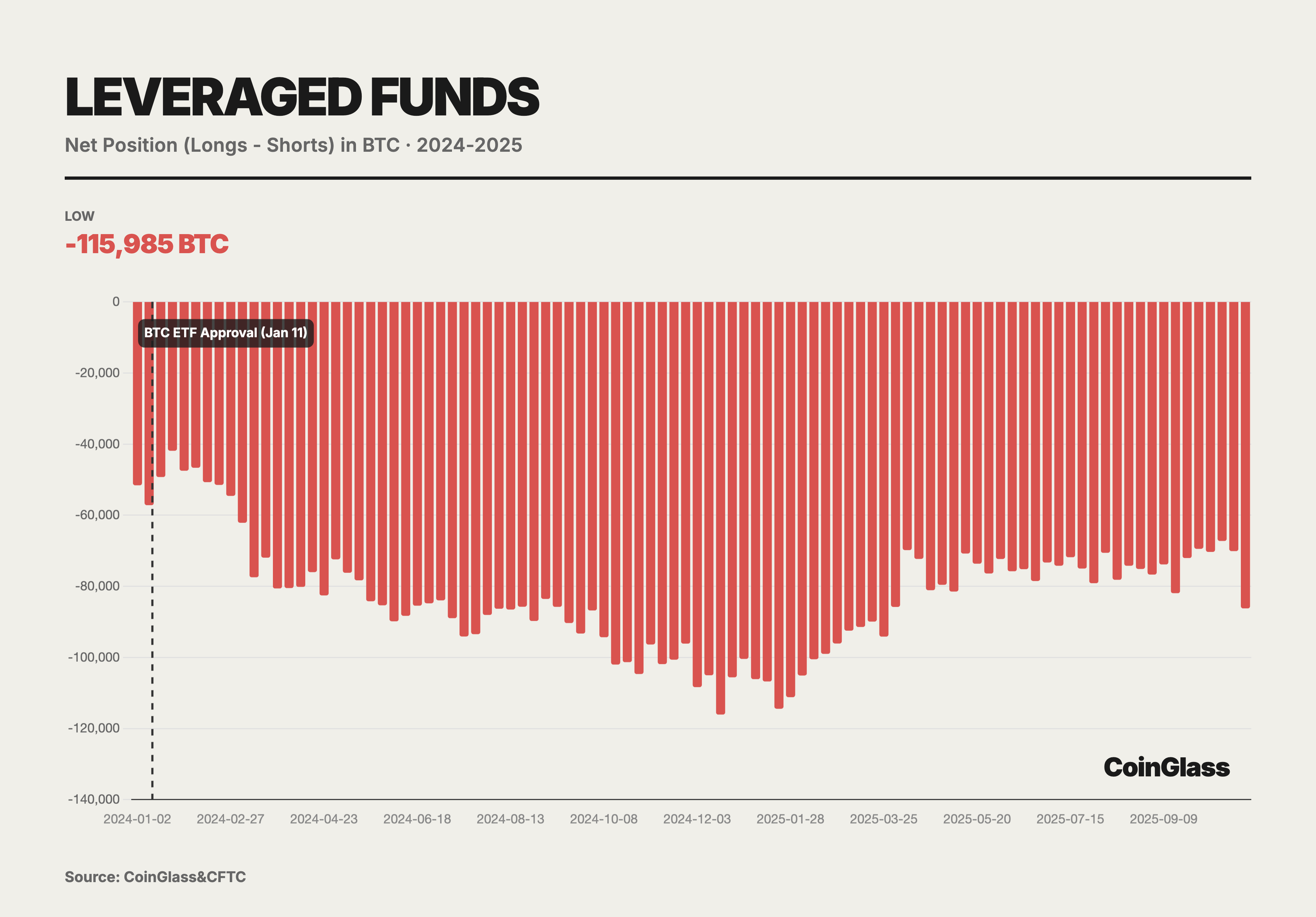
Currently, net short positions held by leveraged funds have reached approximately 14,000 contracts. In-depth analysis reveals that this phenomenon is a direct product of the Basis Trade. Leveraged funds purchase BTC in the spot market or via ETFs while simultaneously selling an equivalent quantity of futures contracts on CME. This portfolio construction is Delta-neutral, designed specifically to capture the basis yield generated when futures prices exceed spot prices. Consequently, as capital inflows into spot ETFs have increased, the short positions held by leveraged funds have risen synchronously. This correlation demonstrates that these short positions do not represent directional betting against the asset; rather, they serve to hedge the long inventory necessitated by spot ETFs. At their peak, leveraged funds held net short positions amounting to 115,985 BTC, effectively acting as the primary liquidity providers and conduits for the spot ETF market.
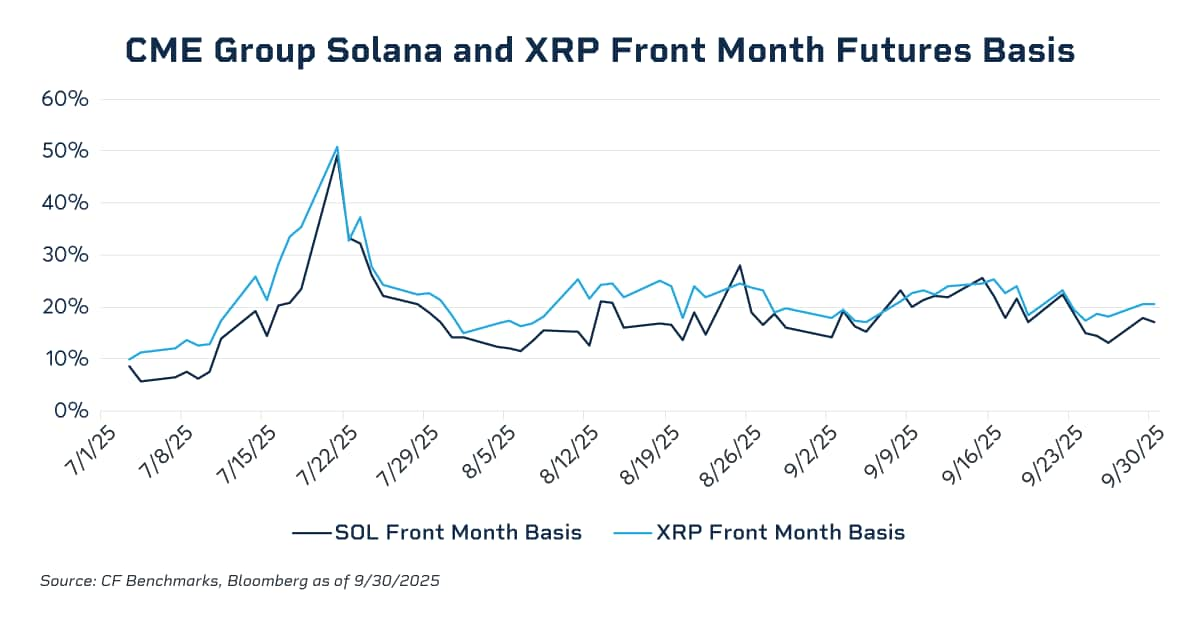
Data indicates that the annualized basis for front-month contracts surged to the 20–25% range during the bull market of November 2024, whereas it compressed to near zero during the deleveraging period in Q1. In July 2025, the annualized basis for SOL and XRP near-month futures contracts temporarily soared to nearly 50%, a level significantly higher than that typically exhibited by BTC futures. This disparity clearly exposed a lack of effective cross-market arbitrage forces in the relevant markets. In the absence of high-liquidity, regulated spot investment vehicles, institutional capital found it difficult to deploy "cash-and-carry" arbitrage structures (short futures/long spot) at scale; consequently, it was unable to exert sustained suppression on excessive basis premiums. With the launch of SOL and XRP Spot ETFs under a universal listing regulatory framework, this structural void was partially filled, providing the necessary spot vehicles and liquidity foundation for compliant institutional capital to enter the market and compress futures basis through arbitrage. Following the CFTC's approval of spot trading, it is highly probable that margin offsetting between spot and futures will be realized in 2026. This development would unlock billions of dollars in idle capital, drastically enhancing market leverage efficiency. By then, the frictional costs of basis trading will drop to historical lows, and basis levels may further converge toward those seen in traditional commodities markets.
In November 2025, the Average Daily Volume (ADV) of the CME cryptocurrency complex reached a historic 424,000 contracts, representing a notional value of $13.2 billion—a year-on-year increase of 78%. This figure surpassed any single-month performance in 2024 and approached levels seen during the peak of the 2021 bull market; however, its composition was healthier, driven more by institutional hedging and arbitrage rather than pure retail speculation.
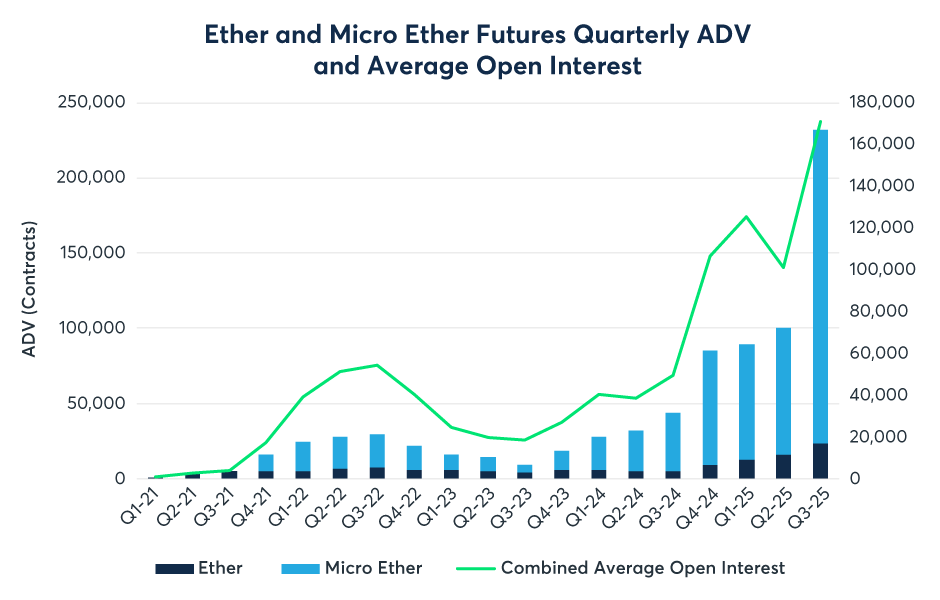
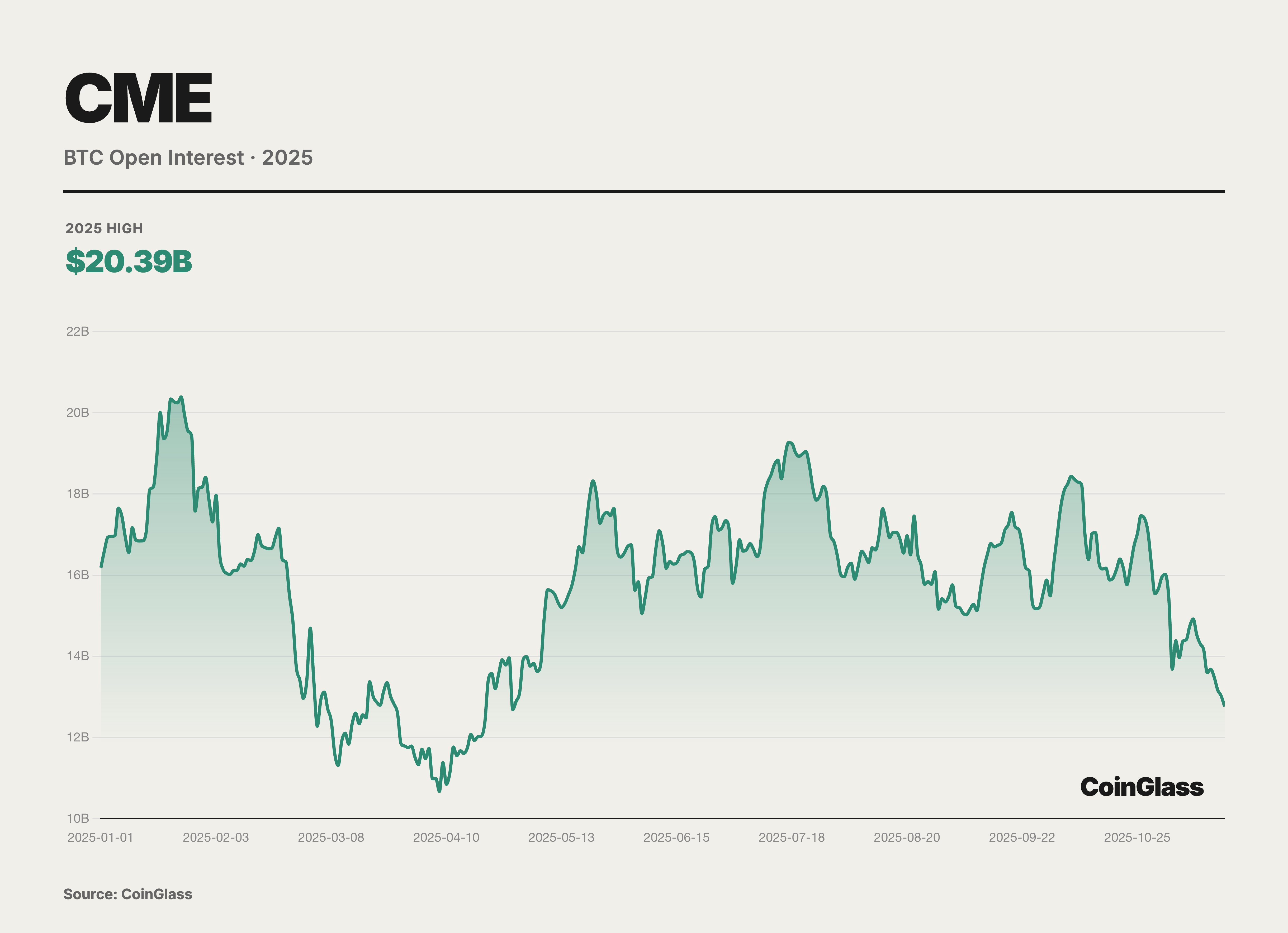
While BTC retained absolute dominance in terms of nominal Open Interest, 2025 marked a year of explosive liquidity growth for ETH derivatives. Data indicates that the Average Daily Volume (ADV) of ETH futures surged by 355% year-on-year in the third quarter, far outpacing the growth rate of BTC. The passage of the GENIUS Act in July 2025 removed the final compliance barrier for traditional financial institutions to enter the market via a policy breakthrough, directly driving the CME Cryptocurrency Complex to set a record daily average Open Interest of $31.3 billion in Q3. Micro contracts continued to serve as a cornerstone of liquidity; in Q3, the ADV of Micro Ether futures (MET) reached a staggering 208,000 contracts. Broker data suggests that many mid-sized hedge funds and family offices favored Micro contracts for position adjustments to more precisely match the size of their spot investment portfolios, thereby avoiding the excessive granularity associated with standard contracts (5 BTC / 50 ETH).
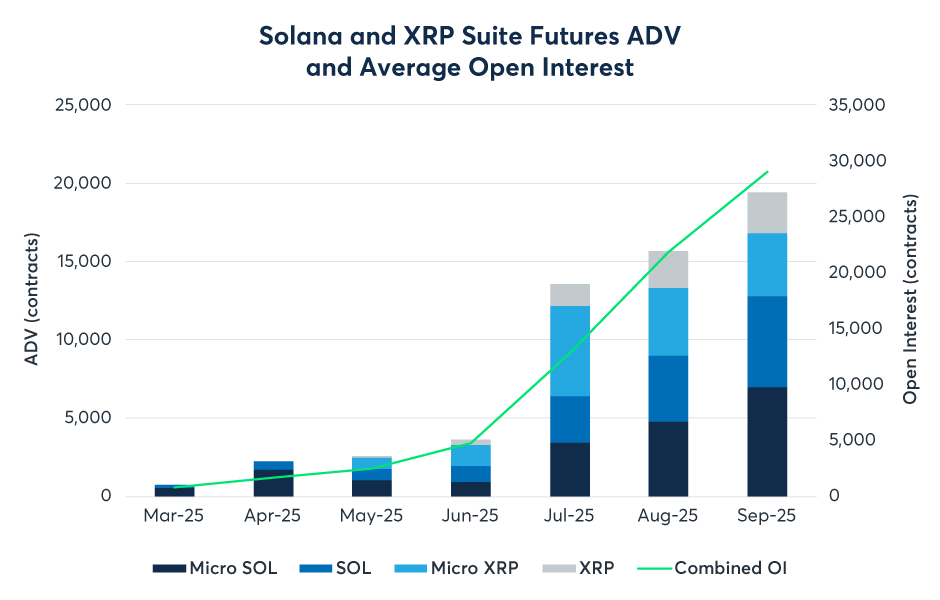
For a long time, the CME functioned effectively as a duopoly market restricted to BTC and ETH. However, this paradigm was disrupted in 2025. With the introduction of SOL and XRP futures and options, the CME formally entered a multi-asset era. As a potent contender for the status of the third-largest asset, SOL futures have delivered remarkable performance since their launch in March. By Q3, cumulative trading volume reached 730,000 contracts, representing a notional value of $34 billion. Even more significantly, the Open Interest (OI) for SOL futures rapidly surpassed $2.1 billion in September, setting a record for the fastest doubling of open interest for a new contract. Meanwhile, XRP futures have traded 476,000 contracts since their launch in May. Furthermore, the XRP options launched on October 13 became the market's first such product regulated by the CFTC. This development signifies that institutional investors no longer equate cryptocurrency exclusively with BTC. Institutions have begun to seek compliant hedging channels for assets like SOL and XRP, which possess distinct risk-return profiles; this foreshadows increased activity by multi-strategy crypto hedge funds on the CME in the future.
2.DAT
At the commencement of Fiscal Year 2025, the Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2023-08 issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) officially took effect. This regulatory change served as the cornerstone for the explosive financial performance of the Digital Asset Treasury (DAT) sector this year. The new standard mandates that entities measure specific crypto assets at fair value, with changes in fair value recognized directly in current net income. Digital Asset Treasury (DAT) refers to listed companies that systematically migrate a substantial portion of their treasury reserves—far exceeding daily operational needs—from cash and short-term debt to digital assets such as BTC, ETH, and SOL. These entities treat crypto assets as a core allocation on the balance sheet rather than as peripheral speculative positions. Unlike spot ETFs, DATs are not passive tracking instruments but corporate entities with full operational control and capital maneuvering capabilities. Corporate management can utilize methods such as convertible notes and At-The-Market (ATM) equity offerings to execute accretive financing, continuously increasing the quantity of digital assets per share, thereby creating the so-called "DAT Flywheel" effect. When the stock price trades at a premium relative to Net Asset Value (NAV), the company issues additional shares to purchase more digital assets; this dilutes equity while enhancing the coins-per-share metric, which in turn supports or even amplifies the premium.
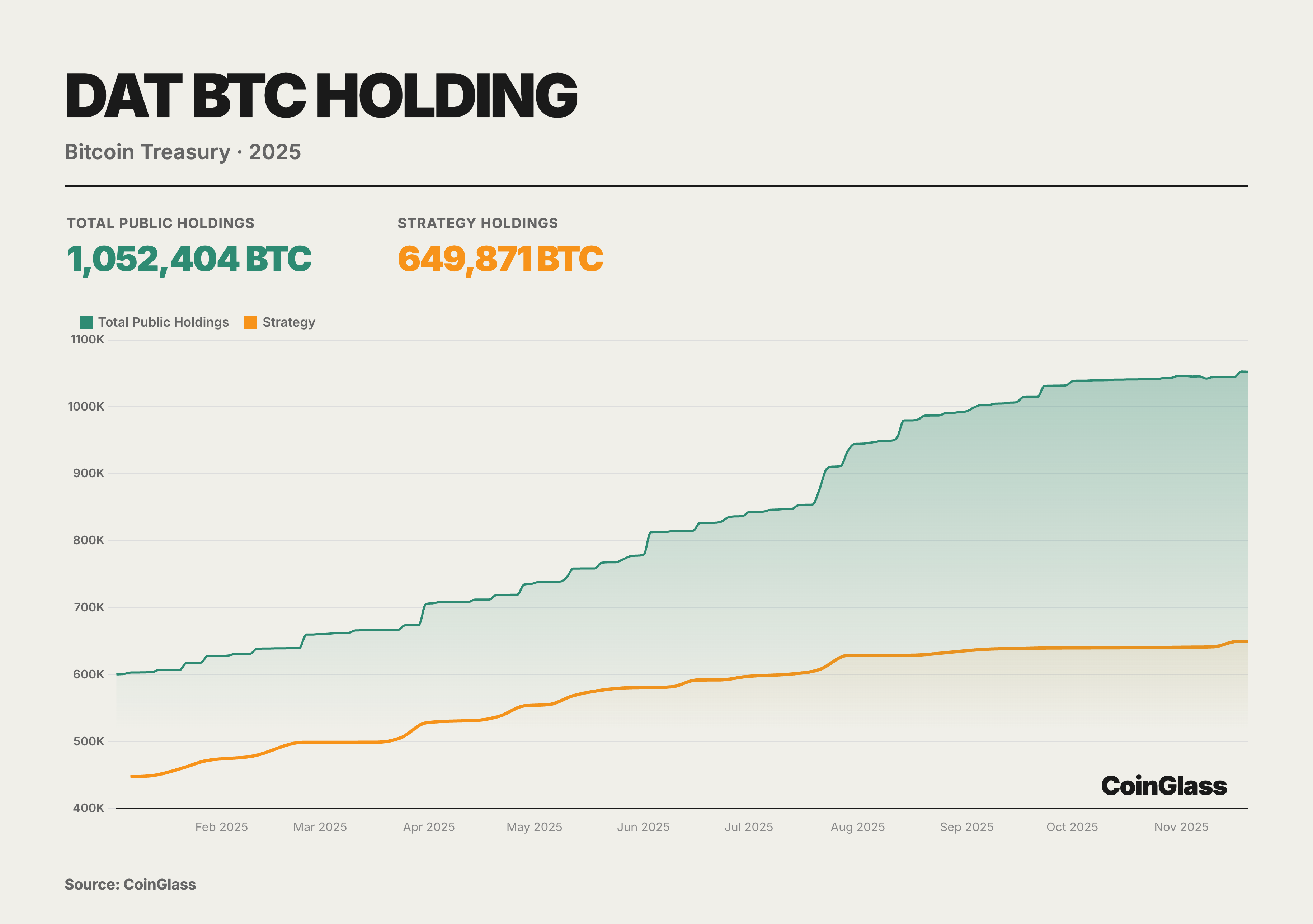
Throughout 2025, the BTC holdings of public DAT companies followed a nearly monotonic upward trajectory, growing from an aggregate of approximately 600,000 BTC at the beginning of the year to about 1.05 million BTC by November, accounting for roughly 5% of the total theoretical supply of BTC. Among them, "Strategy" alone increased its holdings from approximately 447,000 BTC to about 650,000 BTC. While it remains the irreplaceable core of the treasury sector in absolute terms, its market share slid from approximately 70% to just over 60%, indicating that the incremental growth was driven more by small and mid-sized DATs.
During the second and third quarters, various DAT models entered the market en masse, pushing total BTC holdings past the one-million mark. By the fourth quarter, although net capital inflows plummeted from their highs and DAT share premiums were significantly compressed, the curve merely exhibited a deceleration in slope rather than a directional reversal; no systemic deleveraging or forced position reduction occurred. This trend illustrates that the so-called "bubble burst" was primarily a repricing at the equity level rather than a disintegration of BTC positions on the asset side. DATs have evolved from a thematic trade into a structural buying tier within the regulatory framework, forming a supply-side BTC buffer locked in by corporate governance, accounting standards, and information disclosure regimes. Concurrently, the industry structure has evolved from "single-whale dominance" to a "mega-whale + long-tail group" dynamic. The locus of risk has substantively shifted from the token price itself to the financing structures, corporate governance, and regulatory impacts on individual DATs. The key to analyzing the DAT sector lies not in predicting short-term BTC fluctuations, but in understanding the underlying financing structures, derivatives exposures, and macro-hedging logic of these companies. As 2026 approaches, with the impending MSCI index review and potential shifts in global monetary policy, the volatility test for DAT companies has only just begun.
3.Options Market
The core narrative of the options market for this year is defined by two milestone events that collectively reshaped the logic of pricing power for global digital assets. First, Coinbase, the largest compliant exchange in the United States, completed the acquisition of the offshore options giant Deribit for $2.9 billion. This acquisition not only marks the integration of crypto-native liquidity by a traditional compliant exchange but also redefines the infrastructure landscape of global derivatives trading. Second, the rise of BlackRock's IBIT ETF options—which surpassed the long-standing hegemon Deribit in Open Interest for the first time by the end of the third quarter of 2025—signifies that traditional financial capital now formally stands on equal footing with crypto-native platforms regarding volatility pricing power. Prior to this shift, Deribit had enjoyed a near-monopolistic advantage, controlling approximately 85% of the global crypto options market share as of the end of 2024.
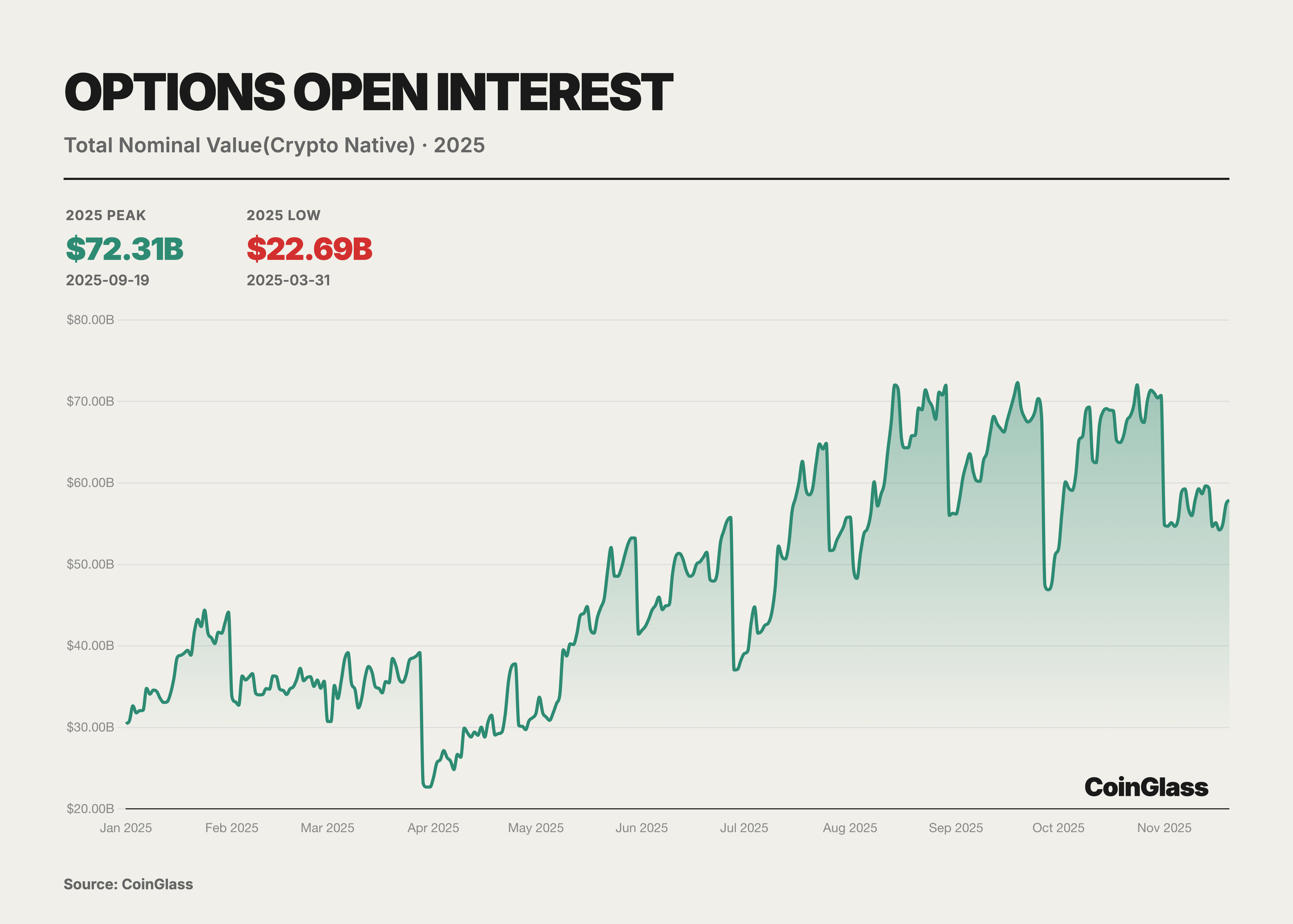
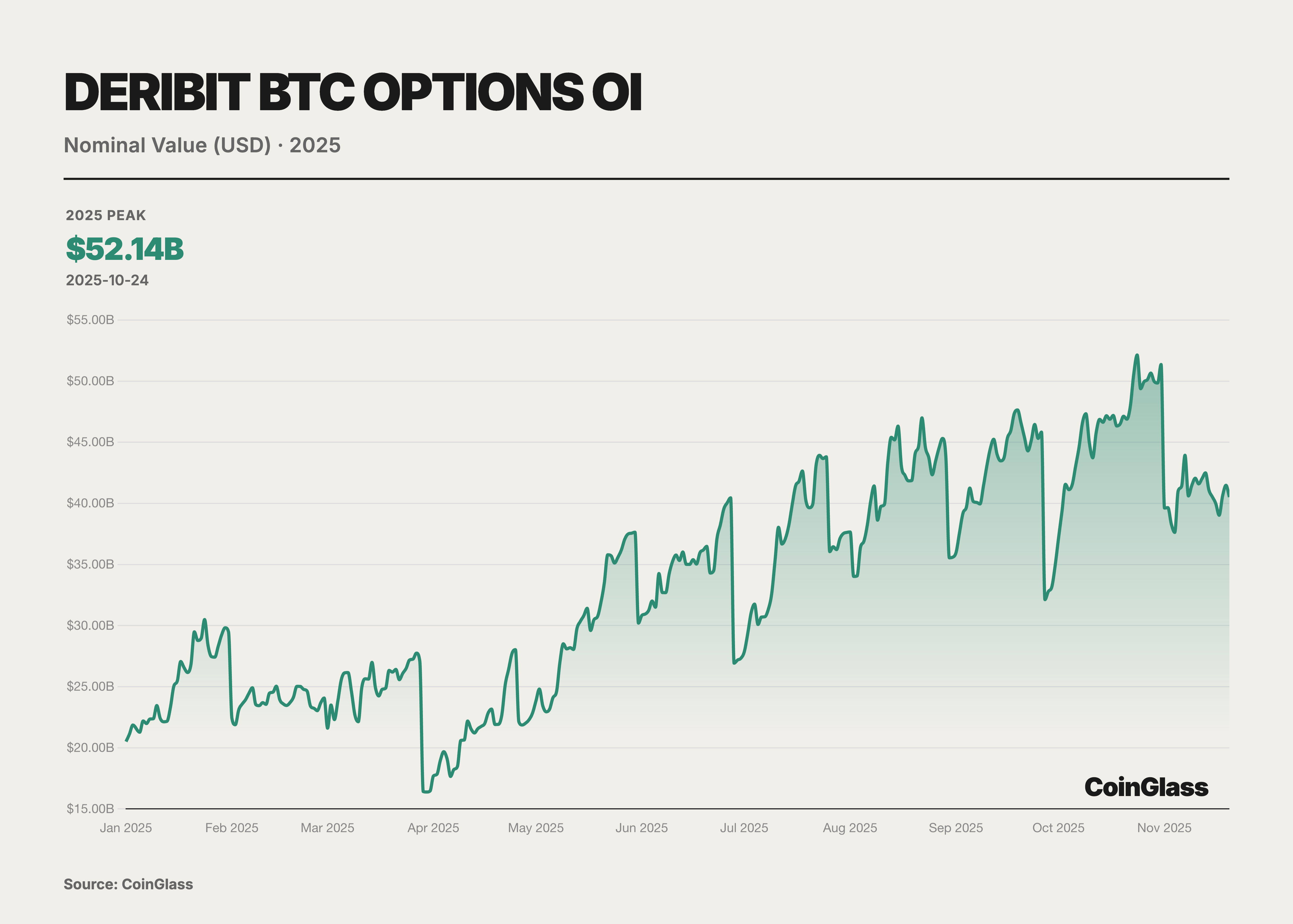
Throughout the year, the intervention of traditional financial institutions served as a watershed moment for the evolution of the options market. As the U.S. regulatory environment evolved, numerous Wall Street institutions launched BTC ETFs and associated option products. Particularly notable was BlackRock's IBIT, which commenced options trading in November 2024 and rapidly emerged as a new titan in the BTC options market during 2025. Overall, the market landscape in 2025 exhibited a "dual-track" characteristic: on one side were crypto-native platforms represented by entities such as Deribit, and on the other were traditional financial channels represented by ETF options like IBIT.
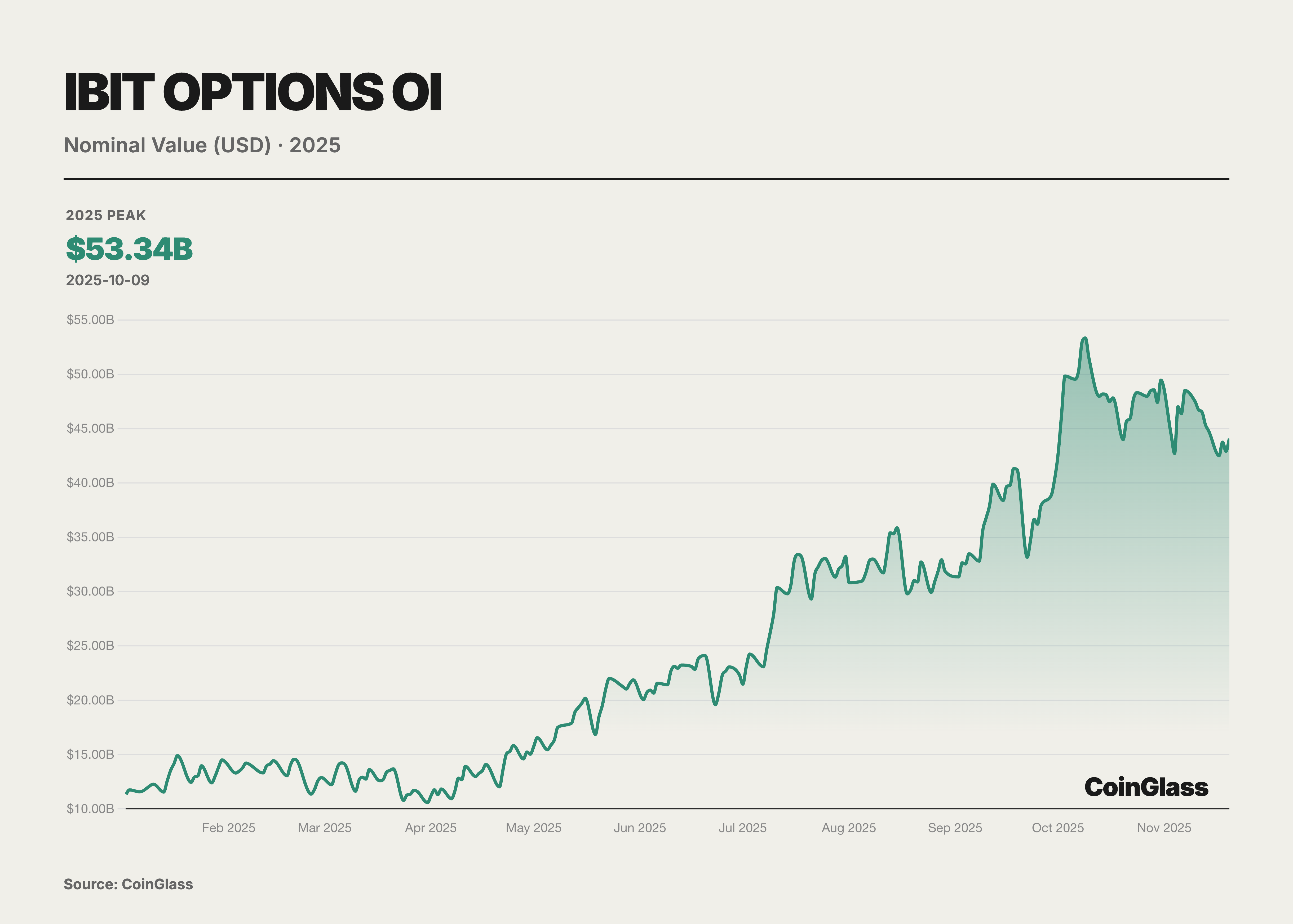
BlackRock's IBIT ETF options have surged prominently, mounting a direct challenge to Deribit. As a spot BTC ETF listed on Nasdaq in the United States, IBIT saw its Open Interest skyrocket within less than a year of its options launch in late 2024. By November 2025, IBIT had established itself as the world's largest vehicle for BTC options trading, superseding Deribit's long-standing dominance. The success of IBIT options underscores the colossal impact of traditional financial forces: a multitude of institutional investors, previously restricted by regulations from participating in offshore platforms, accessed the BTC options market via IBIT, injecting massive capital and demand. Furthermore, the credibility and compliance frameworks of major asset managers backing IBIT, such as BlackRock, have attracted a greater number of conservative institutions to utilize options for BTC risk exposure management. As of November 2025, standing as the largest spot BTC ETF with Assets Under Management (AUM) reaching $84 billion, IBIT provided substantial spot support and a foundational liquidity base for the options market, unequivocally demonstrating the robust market demand for spot ETF options.
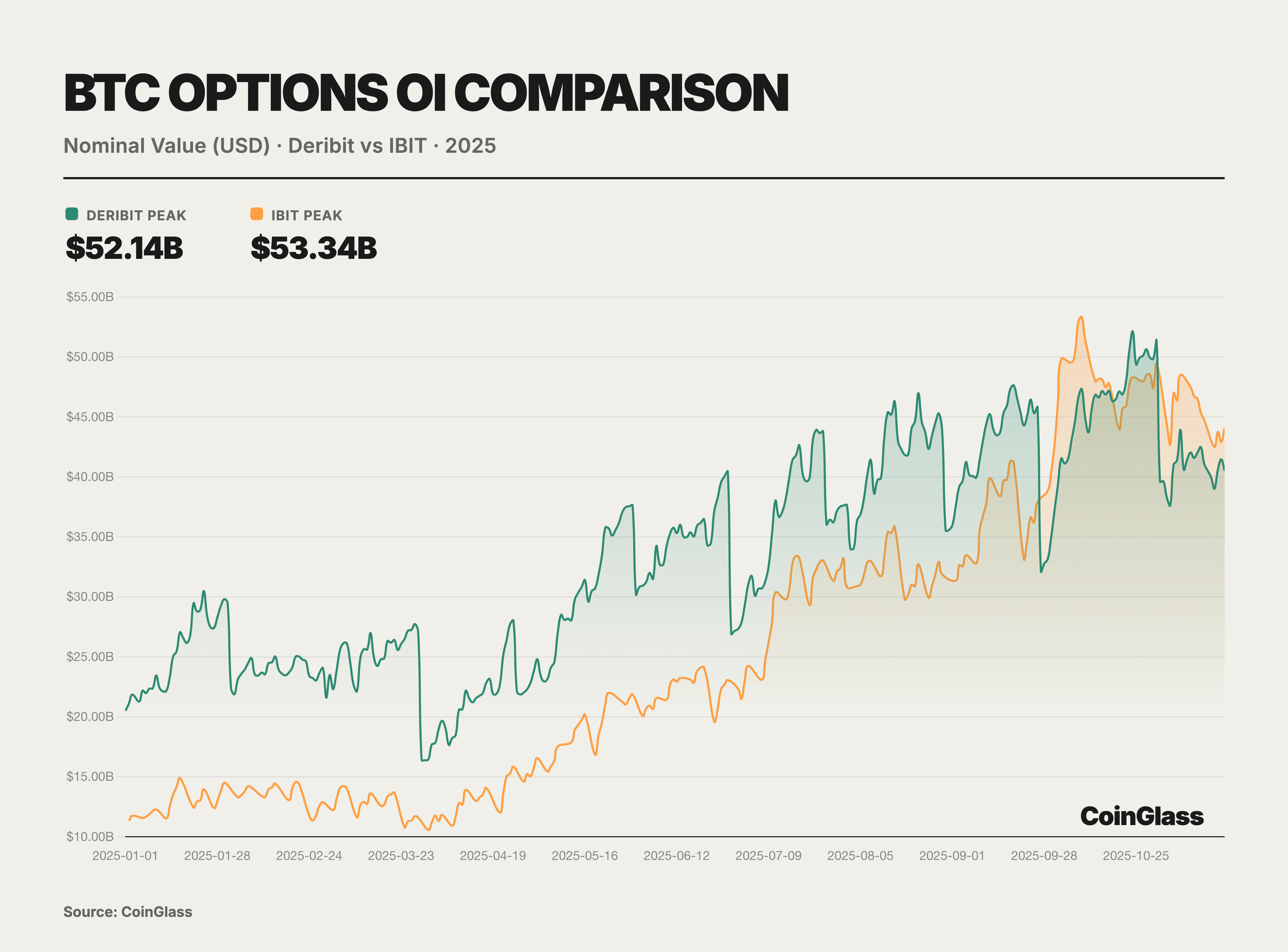
Beyond Deribit and IBIT, the remaining segment of the BTC options market—accounting for less than 10%—is partitioned among the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) and a select few crypto trading platforms. As a traditional regulated venue, the CME offers options trading based on BTC and ETH futures. Despite some growth in market share over recent years, CME accounted for only approximately 6% of global BTC options Open Interest (OI) as of the third quarter of 2025. This reflects the limited market appeal of futures-based options compared to more flexible crypto-native platforms and ETF options. Centralized exchanges such as Binance and OKX have also attempted to launch BTC and ETH option products in recent years; however, user participation has remained relatively tepid. Trading volumes on these exchanges are predominantly concentrated in perpetual contracts and futures, with the options business constituting only a fraction of their derivatives landscape. Platforms like Bybit also offer USDC-settled options trading, yet their overall market share remains similarly constrained. Other exchanges, represented by OKX and Binance, collectively contributed only about 7% to the total BTC options Open Interest.
Overall, the crypto options market in 2025 exhibited a highly concentrated landscape: crypto-native platforms (represented by Deribit) continued to dominate non-ETF instruments such as ETH, while traditional financial platforms (represented by IBIT) came from behind to lead in BTC options. Under this duopoly structure, the roles of other players are becoming increasingly marginalized. Notably, regarding ETH options, due to the absence of a spot ETF option product comparable to IBIT, Deribit remains virtually the sole center of ETH options liquidity, commanding a market share exceeding 90%. This signifies that Deribit's dominance in the ETH options market remained unshakable in 2025, with IBIT's impact primarily confined to the BTC sector. Looking ahead, with the approval for the issuance of ETH spot ETF options granted in April 2025, the possibility cannot be ruled out that ETH ETF options will subsequently be launched and gradually enter the competitive fray. However, as of November 2025, the ETH options market remains the territory of crypto-native exchanges, with no traditional institutional-grade competitor comparable to IBIT having yet emerged.
IV.DeFi
- PerpDEX
The year 2025 was a spectacular year for Perpetual DEXs (Perp DEXs). Trading activity across the entire market experienced explosive growth, continuously setting new historical records. Monthly trading volume surpassed $1.2 trillion for the first time in October, bringing the cumulative annual on-chain derivatives trading volume to a multi-trillion dollar scale. This surge in trading volume and the corresponding expansion of market share were driven by a confluence of factors, including performance breakthroughs, rising user demand, and shifts in the regulatory environment. Retail investors, institutional trading desks, and venture capital funds alike turned their gaze toward this burgeoning sector in 2025.
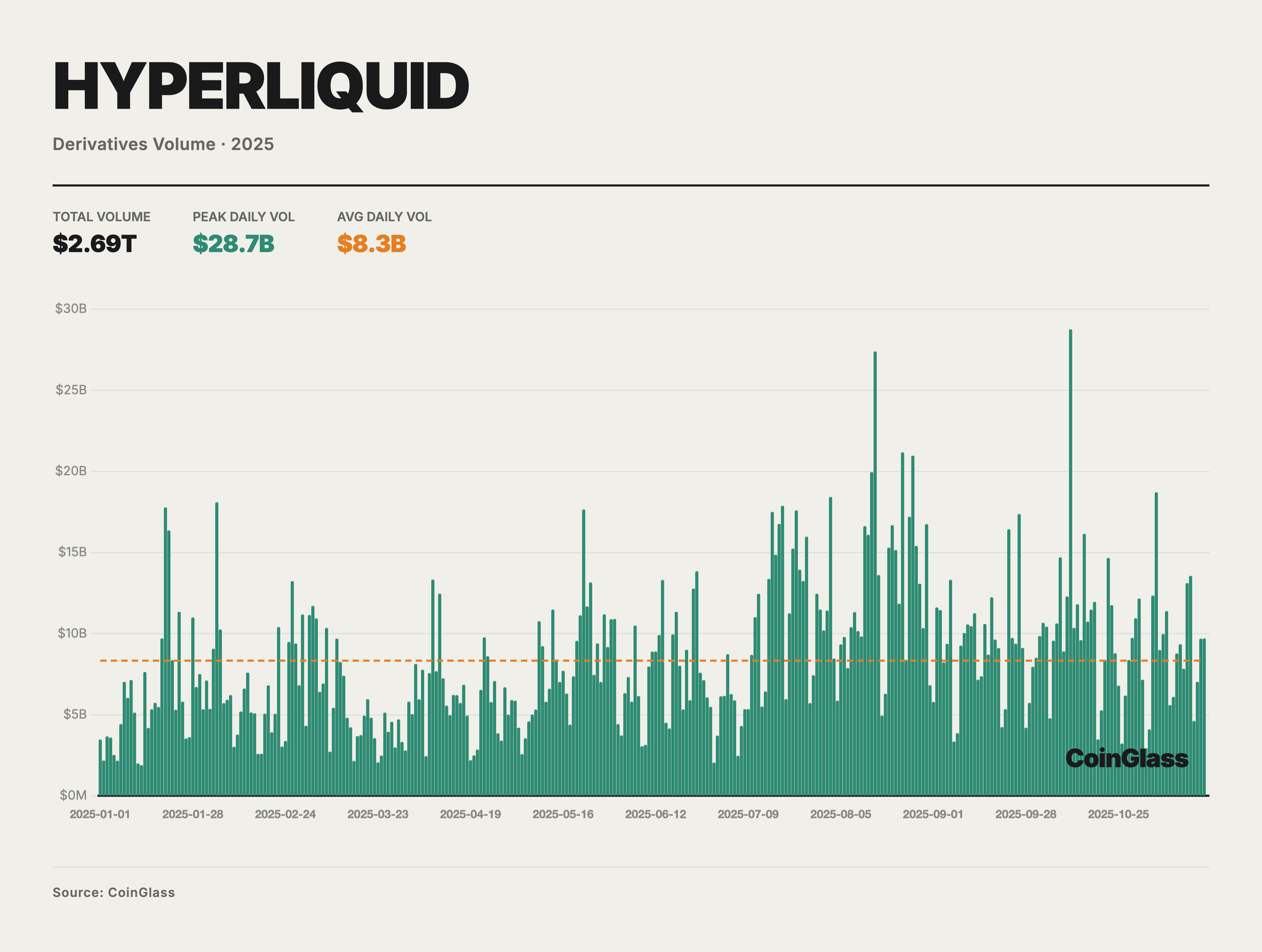
Hyperliquid stands as the undisputed leader of the PerpDEX market in 2025. throughout the first half of the year, the platform nearly dominated the entire sector, with its market share reaching as high as 70–80% at times. In May, Hyperliquid's share of on-chain perpetual contract trading volume peaked at approximately 71%. This staggering volume effectively made Hyperliquid synonymous with the PerpDEX market during the first half of 2025.
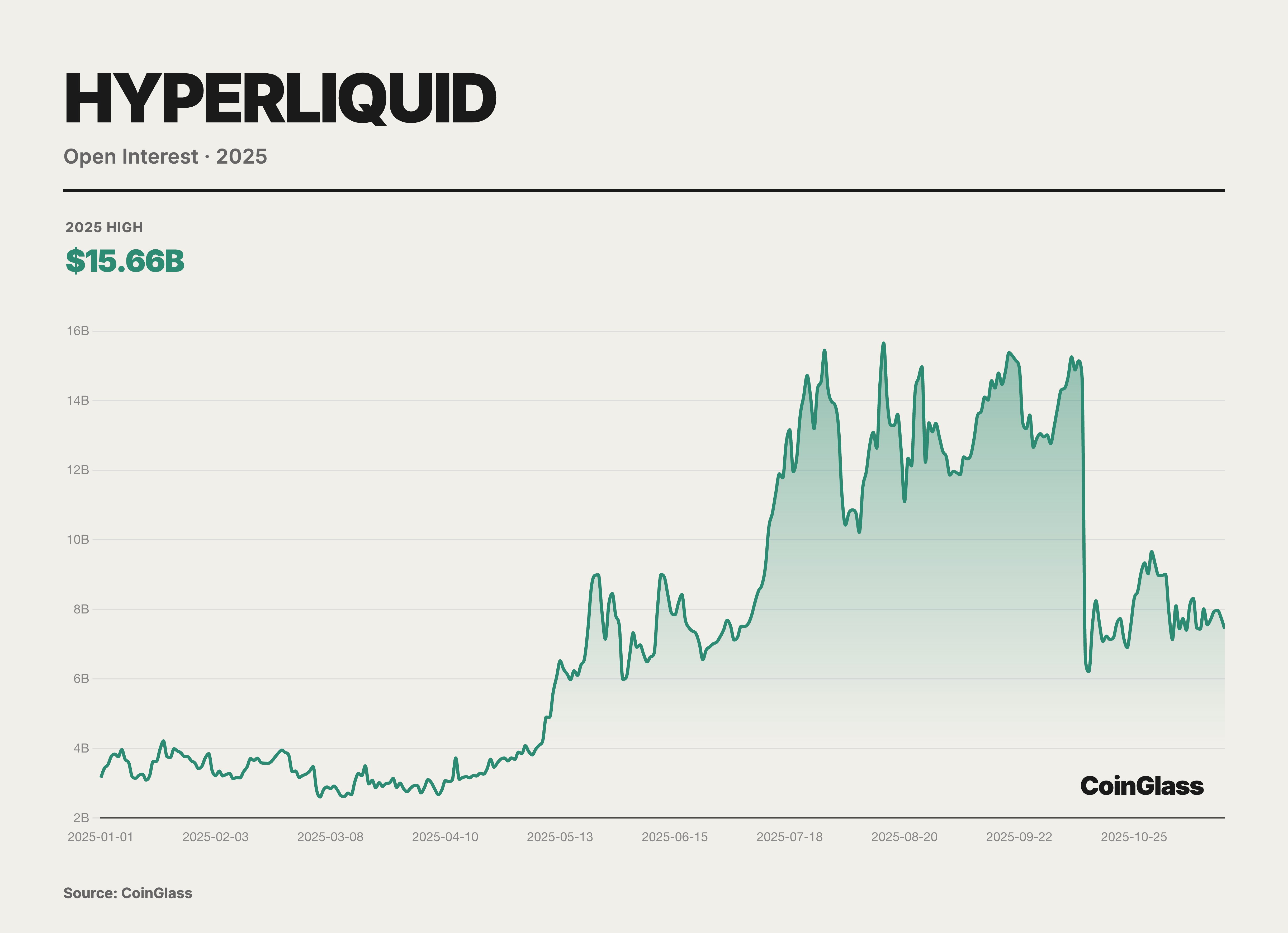
Hyperliquid has not only attracted massive trading volumes but has also amassed a colossal scale of Open Interest. Data from October 2025 reveals that the value of its perpetual contract open interest reached $15 billion, accounting for approximately 63% of the total holdings across major decentralized perpetual platforms. This metric indicates that substantial capital has chosen to remain stationed on Hyperliquid over the long term, reflecting a high degree of trader confidence in the platform's liquidity and stability.
Distinguished from traditional Ethereum Layer 1 or general-purpose public chains, Hyperliquid has constructed a custom Layer 1 blockchain specifically engineered for high-frequency derivatives trading. This chain utilizes a proprietary HyperBFT consensus mechanism capable of processing 200,000 orders per second with transaction confirmation latency as low as 0.2 seconds. This performance surpasses that of many centralized exchanges, positioning Hyperliquid as the first exchange to achieve near-CEX speed and liquidity on-chain. By adopting a fully on-chain Central Limit Order Book (CLOB) model, the platform guarantees market depth and quote quality, allowing professional traders to enjoy a matching experience comparable to traditional exchanges.
Although Hyperliquid stood as the sole hegemon in the first half of 2025, the aggressive entry of new participants in the second half shifted the PerpDEX market structure from a "single superpower" to a "multi-polar" landscape. Entering the third and fourth quarters, Hyperliquid's market share experienced a marked decline—dropping from mid-year levels of approximately 70–80% to 30–40% by year-end. According to on-chain data, Hyperliquid's share of trading volume fell to about 20% in November, while rising stars such as Lighter and Aster surged rapidly: in that month, Lighter captured approximately 27.7%, Aster 19.3%, and another dark horse, EdgeX, reached 14.6%. This signifies that a market once dominated by Hyperliquid evolved into a competitive arena with multiple strong contenders within just a few months. Substantial trading incentives, differentiated product strategies, and capital support drove the rise of these challengers, pushing competition across the entire PerpDEX sector into a fever pitch during the latter half of 2025.
2.Prediction Markets
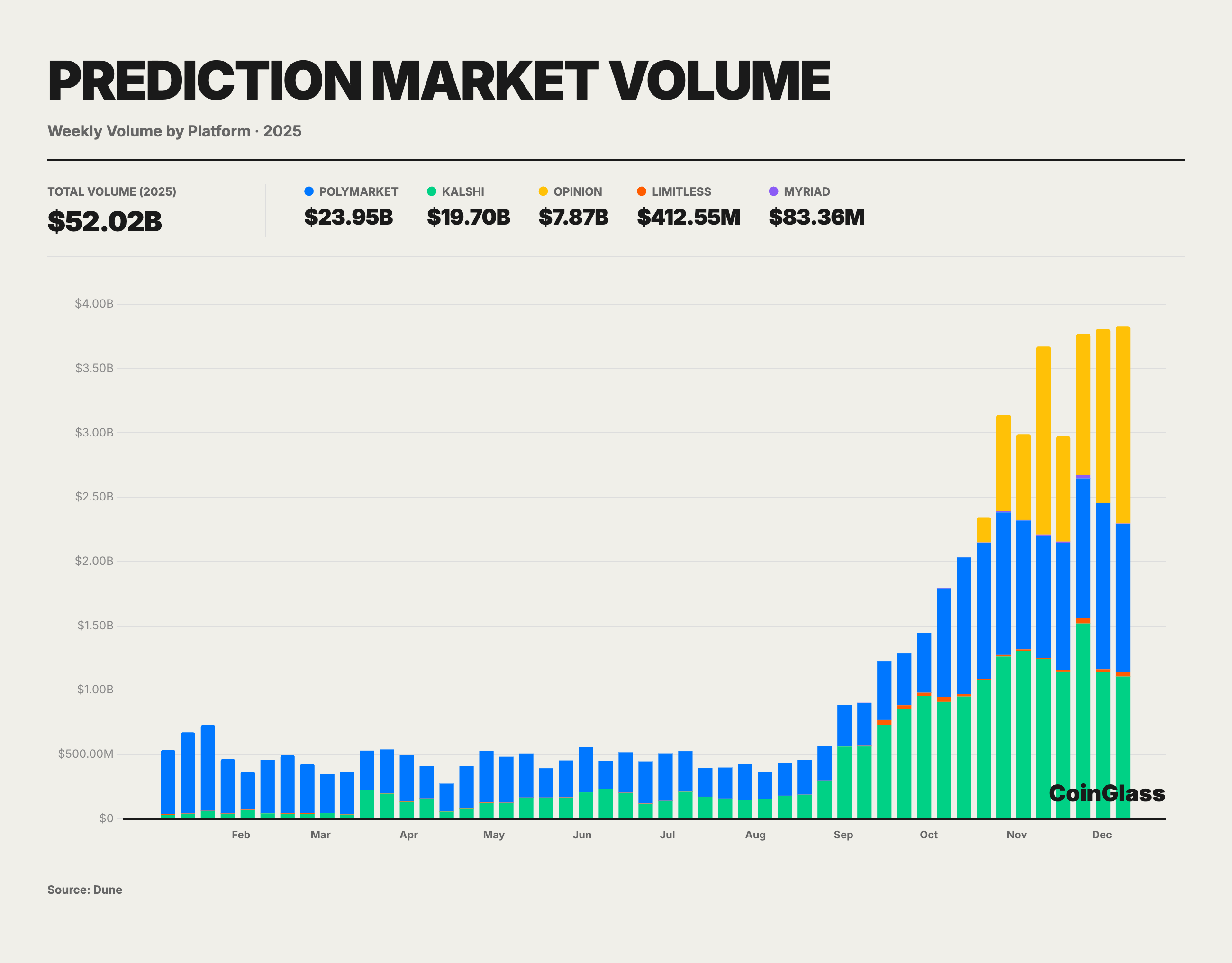
The crypto prediction market witnessed explosive growth in 2025, with cumulative trading volume from January to November reaching approximately $52 billion, significantly surpassing the peak levels observed during the 2024 U.S. election. As the world's largest prediction market platform by volume, Polymarket alone recorded a cumulative trading volume exceeding $23 billion in 2025.
The platform's user engagement metrics saw remarkable surges: Daily Active Users (DAU) approached 60,000, a figure that has nearly tripled since the beginning of the year, while peak Monthly Active Users (MAU) were estimated to exceed 450,000, demonstrating a significant elevation in public participation. Currently, the total number of registered trading users on Polymarket stands at approximately 1.35 million, reflecting the rapid expansion of its user base over the past year.
This massive user base and ample liquidity have enabled the cumulative turnover of single contracts in multiple popular markets to reach the scale of hundreds of millions of dollars. These deeply liquid markets can now accommodate capital inflows and outflows in the tens of millions without causing drastic slippage. Consequently, in scenarios characterized by high liquidity, reliable settlement, and clearly defined events, prediction market prices are frequently utilized as supplementary indicators. Notably, during the U.S. election in November 2024, Polymarket's single-day trading volume peaked at nearly $400 million; the platform accurately predicted the election outcome, standing in contrast to the deviations seen in traditional polls. This instance underscored the information aggregation capability and pricing accuracy of decentralized prediction markets regarding major events, laying the foundation for their further progression toward the mainstream in 2025.
3.Web3 Wallets
As the primary interface connecting users to decentralized networks, the strategic importance of Web3 wallets experienced a fundamental leap in 2025. No longer functioning merely as custodial containers for private keys or simple transfer tools, wallets have evolved into comprehensive on-chain traffic gateways integrating Decentralized Identity (DID), asset management, Decentralized Application (DApp) operating systems, and social graphs.
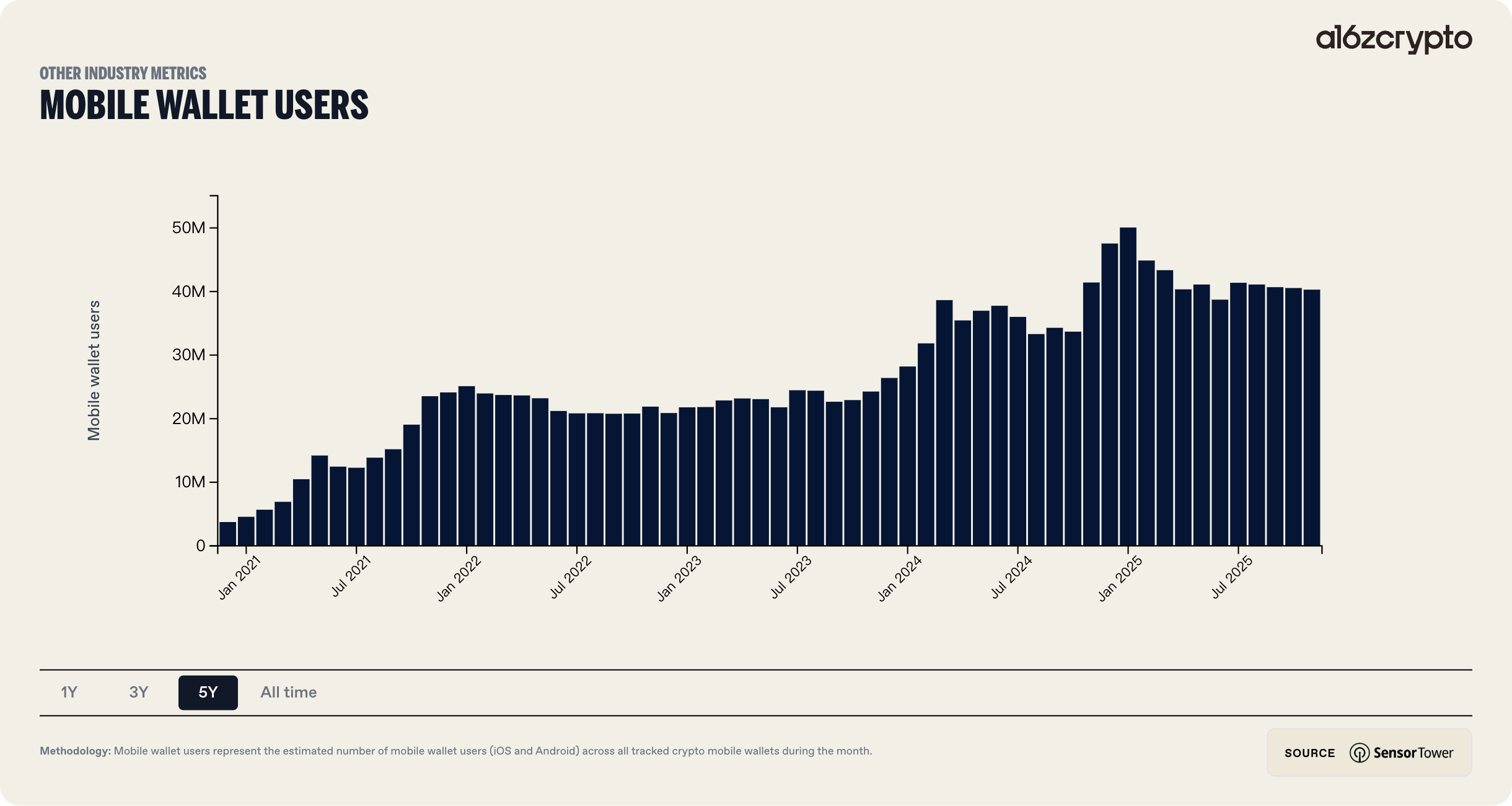
Looking back over the past five years, the morphology of Web3 wallets has undergone a radical transformation. Early wallets demanded an extremely high level of technical literacy from users, who were required to self-manage mnemonic phrases, understand gas fee mechanisms, and manually configure networks. This high barrier resulted in a massive user churn rate; data indicates that historically, over 50% of users abandoned the onboarding process during the wallet setup phase due to its complexity.
The most defining industry characteristic of this year is the large-scale deployment of Account Abstraction and the standardization of Chain Abstraction technologies. The convergence of these two technologies has endowed Web3 wallets with the capability to rival Web2 financial applications in user experience for the first time. Complex private key management, obscure gas fee mechanisms, and fragmented multi-chain liquidity are being encapsulated by intelligent backend protocols, thereby reducing user-perceived friction to historical lows. Meanwhile, the influx of institutional-grade capital has necessitated an upgrade in wallet security architecture. The combination of Multi-Party Computation (MPC) and Trusted Execution Environments (TEE) has become standard among top-tier wallets, fundamentally revolutionizing the fragile security model where "the private key is everything."
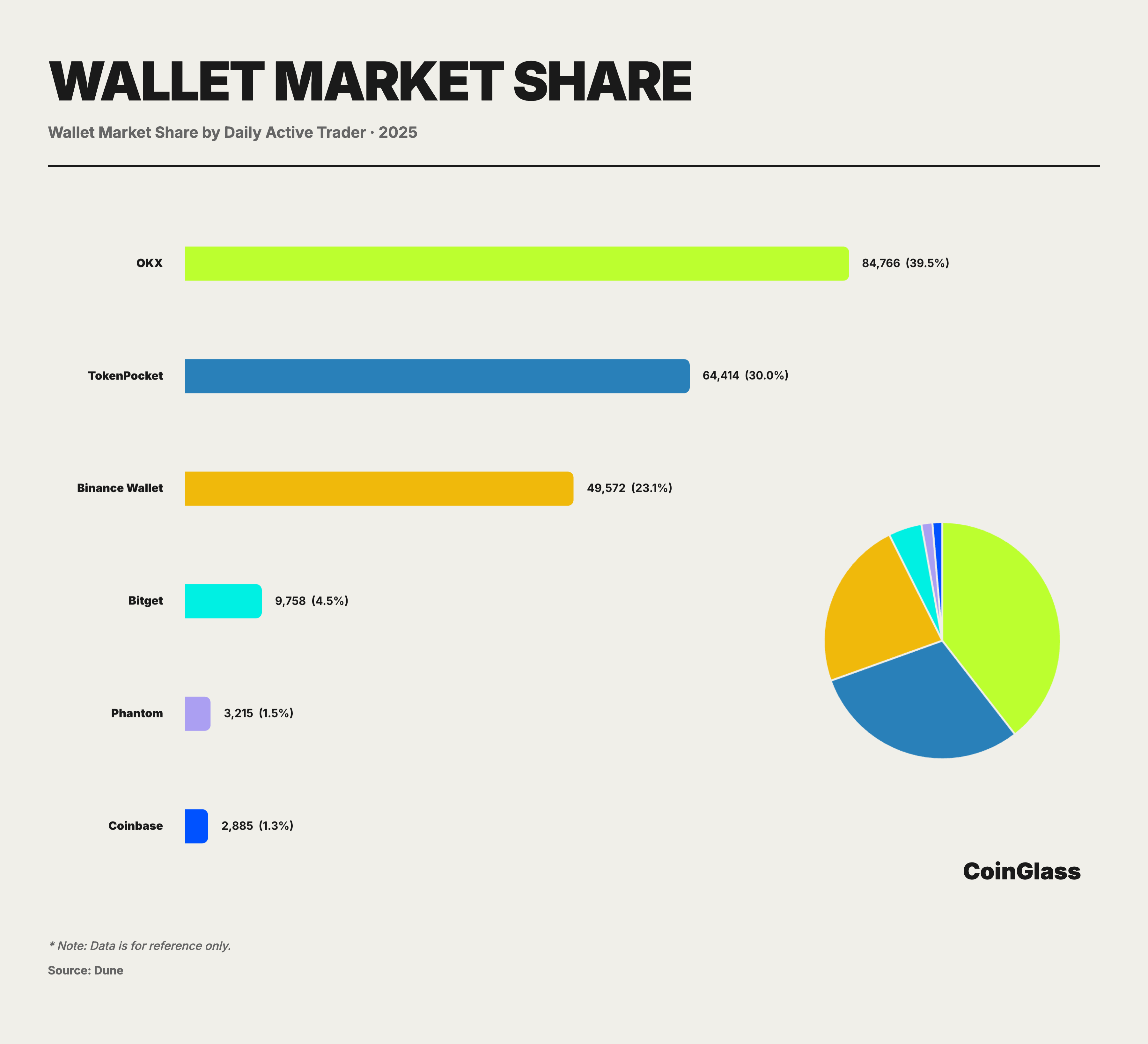
In the market structure of 2025, characterized by "one superpower and multiple strong contenders," the OKX Web3 Wallet is widely recognized as the comprehensive frontrunner of the track, leading the industry in both usability and functional integration through a combination of technological innovation and an all-encompassing ecosystem. As a super-aggregator for Web3 entry, the OKX Wallet boasts over 5 million Monthly Active Users (MAU). Its core design philosophy lies in encapsulating complex on-chain logic behind a minimalist interface; through a unified dashboard, users can easily manage assets distributed across more than 100 public chains without the need to manually add contracts. Simultaneously, the OKX Web3 Wallet stands as one of the industry's earliest products to deeply integrate a DEX aggregator. While many other wallets remained stuck supporting single-chain Swap functions, the OKX Wallet had already internalized multi-chain trading aggregation. Its built-in OKX DEX aggregator covers over 100 public chains, automatically finding the best trading paths for users via intelligent routing. Upon initiating a swap request within the wallet, the aggregator simultaneously calls quotes from multiple DEXs and splits routes to ensure execution at the optimal price with the lowest slippage.
Beyond established leaders like the OKX Wallet, 2025 also witnessed the emergence of rising stars such as the Binance Wallet. The core driver behind the Binance Wallet's sudden prominence in 2025 was the "Binance Alpha" growth strategy: embedding early-stage project discovery and trading directly into the wallet. This allowed users to participate in early-stage projects, airdrops, and Token Generation Events (TGEs) through a path closely resembling centralized products. Officially, Alpha is positioned more as a "discovery and screening pool for pre-listing projects." It enhances transparency and accessibility in processes and converts on-chain participation into higher-frequency trading behavior and retention through task-based and equity-based mechanisms. This Alpha-driven wallet growth was reflected quite directly in the data.
In a different strategic direction, Bitget Wallet placed its bets on PayFi in 2025, bridging on-chain wealth management with real-world consumption while advancing the Wallet Card. Its gas-free "GetGas" feature covers multi-chain gas payments and supports social logins via Google, Apple, and email. The wallet natively integrates Real World Assets (RWAs) like Ondo, allowing for the trading of tokenized U.S. stocks. Furthermore, by offering QR code and card payments alongside "Stablecoin Wealth Management Plus," Bitget Wallet is actively positioning itself as an "Everyday Finance App."
V.Conclusion
The central narrative of the crypto derivatives market in 2025 was a repricing driven by the parallel evolution of institutional capital, compliant infrastructure, and on-chain technology, shifting away from high-leverage retail speculation. Macro liquidity determined the overarching trends, with crypto amplifying volatility as a high-beta asset amidst rate cut expectations and shifting risk appetites, while geopolitical events and policy changes served as triggers. During the year's deleveraging phase, an exogenous shock in October, superimposed on the crowded leverage accumulated in the third quarter, caused a drawdown of over $70 billion in network-wide Open Interest (OI) within two days, resulting in a peak liquidation event reaching the tens of billions.
On the CEX side, amidst an annual trading volume of approximately $85.7 trillion, OI, liquidity depth, and custody became highly concentrated among top-tier platforms. While these leaders enhanced price discovery and execution efficiency, they also amplified compliance, operational, and technical events into systemic risks. Under conditions of declining inventory and thinning order books, this centralization magnified both the marginal thrust during rallies and the liquidity vacuum during crashes. Extreme liquidations exposed the fragility of the "Margin—Liquidation—Insurance Fund—ADL" chain: when insurance funds were under pressure and cross-platform transfers were congested, the non-transparent execution of ADL and position reductions deviating from market prices dismantled hedging legs. This forced neutral portfolios to passively mutate into directional risks, necessitating a complete stress-test overhaul of risk controls centered on liquidation mechanisms and capital accessibility.
Institutionalization became more concentrated in exchange-traded derivatives and the Digital Asset Treasury (DAT) sector. Compliant innovations by CME, such as spot-quoted futures, drove the normalization of basis trading, linking spot ETF demand and futures hedging into a replicable arbitrage chain. Driven by accounting standards and financing tools, DATs formed a balance sheet-based "allocation/financing flywheel." While this made buying pressure more "locked-in," the center of gravity for risk migrated from token prices to financing structures, corporate governance, and regulatory shocks. Concurrently, pricing power in the options market migrated; the M&A consolidation of compliant exchanges and the rise of ETF options concentrated BTC volatility flows into traditional financial channels. On the DeFi side, PerpDEXs approached the CEX experience by relying on high-performance app-chains and intent-centric architectures, moving toward a multi-polar competitive landscape, while account/chain abstraction in prediction markets and wallets pushed discovery, trading, and distribution to the application layer.
In summary, the current derivatives market presents distinct structural opportunities and asymmetric risks. Opportunities lie primarily in the low-risk basis arbitrage space emerging from the integration of compliant spot and derivatives tools (such as ETF options), as well as the functional substitution of traditional centralized liquidity by high-performance on-chain infrastructure (PerpDEX). Conversely, risks are highly concentrated in the potential "double kill" of equity and token prices triggered by a reversal in DAT financing logic, and the hidden dangers of systemic insolvency caused by liquidity mismatches of tail assets within highly concentrated CEX liquidation systems. Looking ahead to 2026, as global regulatory frameworks accelerate toward convergence and the liquidity environment faces potential turning points, the market's core competitiveness will focus on whether trading infrastructure can maintain liquidation resilience within extremely crowded leverage chains, and whether capital can find the most efficient circulation paths between compliant and decentralized realms.
Disclaimer
CoinGlass Technology Co., Limited all rights reserved. COINGLASS, CoinGlass Institutional, and related logos are trademarks of CoinGlass Technology Co., Limited (hereinafter referred to as "CoinGlass") or its affiliates. The views and opinions expressed in this material are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official position or views of CoinGlass. The information and analysis provided herein regarding cryptocurrencies and related topics are for informational purposes only and are intended solely for investors with relevant investment experience. This content does not constitute: (i) an offer or solicitation to invest in, buy, or sell any cryptocurrency, digital asset, financial instrument, or security, or to participate in any specific investment or trading strategy; (ii) accounting, legal, tax, or investment advice or recommendations; or (iii) an official statement by CoinGlass.
Unless otherwise noted, all data in this report is sourced from CoinGlass, covering the period from January 1, 2025, to November 20, 2025. CoinGlass makes no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, timeliness, or reliability of the information in this material, nor regarding the future performance of any cryptocurrency, digital asset, financial instrument, market condition, or economic indicator. The information provided herein is deemed accurate as of the date of publication but may not be updated or revised to reflect subsequent information or changing circumstances. CoinGlass has not independently verified this information and makes no representation regarding its current or long-term accuracy or its suitability for specific situations. Certain statements herein may contain predictions or forward-looking statements, and no guarantee is made regarding the accuracy or realization of such statements. Past performance mentioned in the text is not indicative of future results. Readers should consult their professional advisors before making investment decisions. Furthermore, this content is not directed at, nor intended for use by, any investor or potential investor, and under no circumstances shall it be relied upon as the basis for any decision to purchase or sell any asset.
CoinGlass, its affiliates, and employees may hold financial interests in or have affiliations with certain cryptocurrencies, assets, entities, or services discussed in the text. Any links provided herein are for the convenience of the reader only and do not imply CoinGlass's endorsement or approval of third-party websites or their content. Unauthorized use, reproduction, forwarding, dissemination, or republication of all or part of this content in any form is strictly prohibited without the express permission of CoinGlass. CoinGlass provides data analysis and information services only and does not engage in virtual currency trading, custody, or payment businesses.